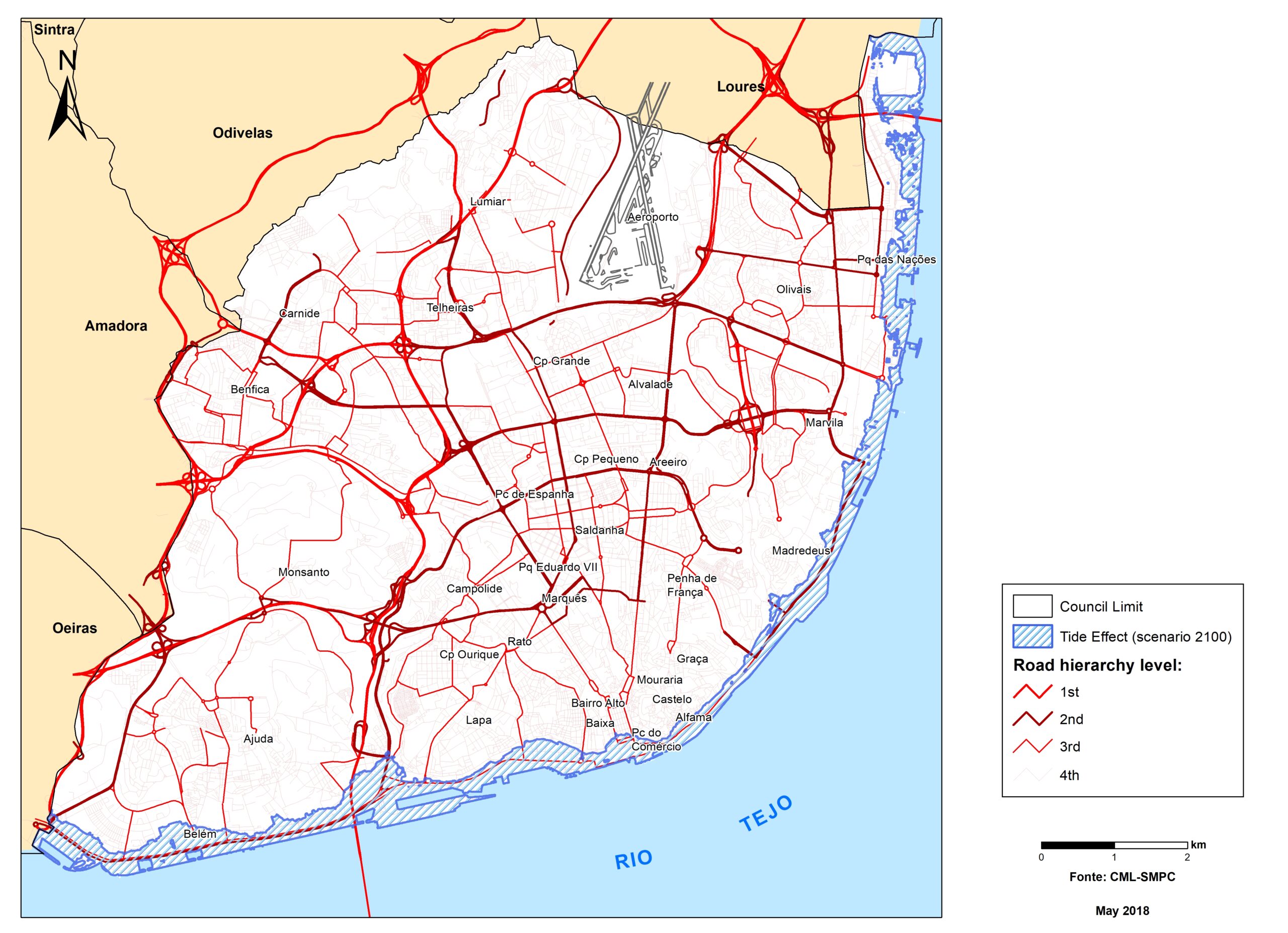
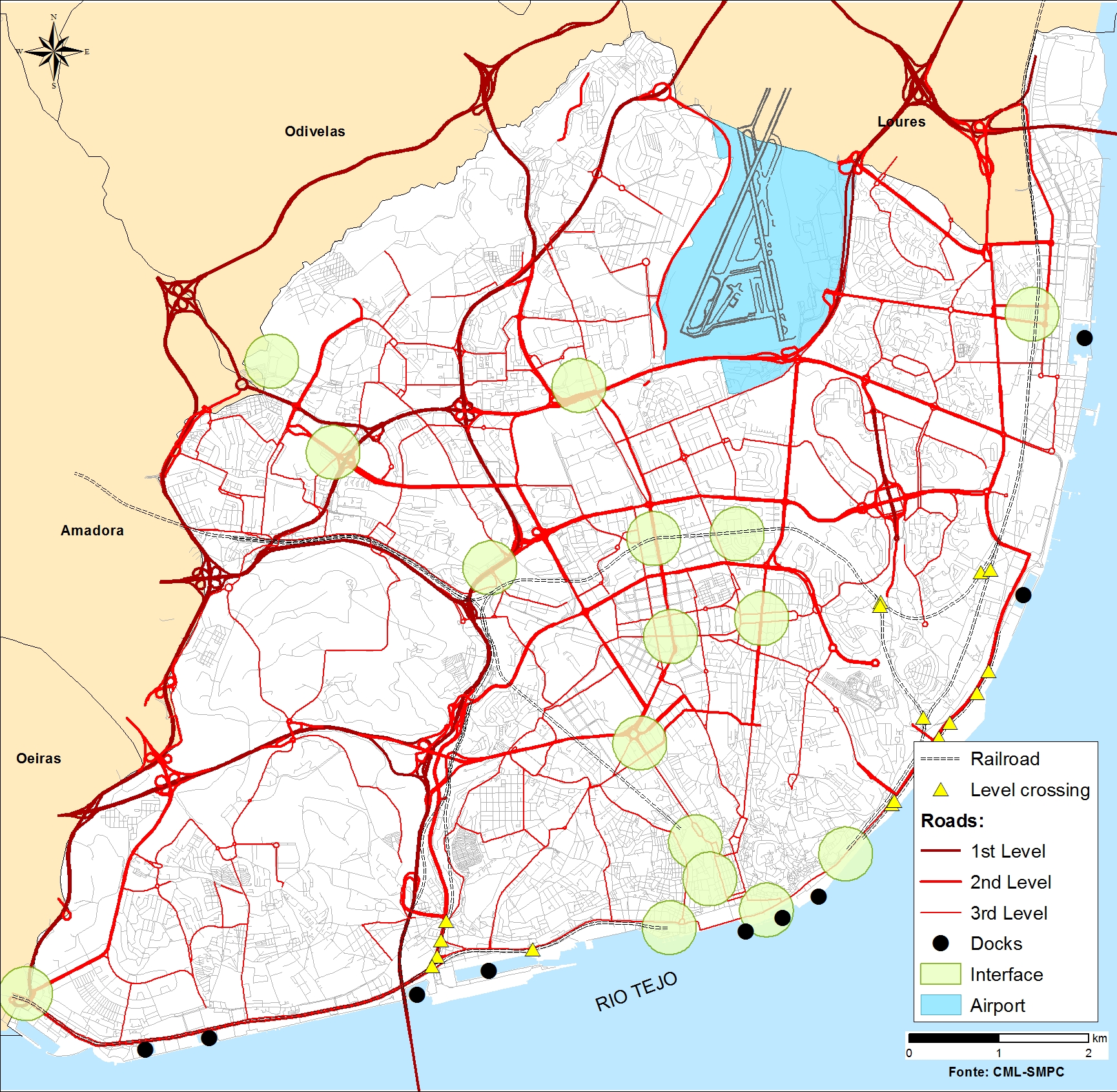
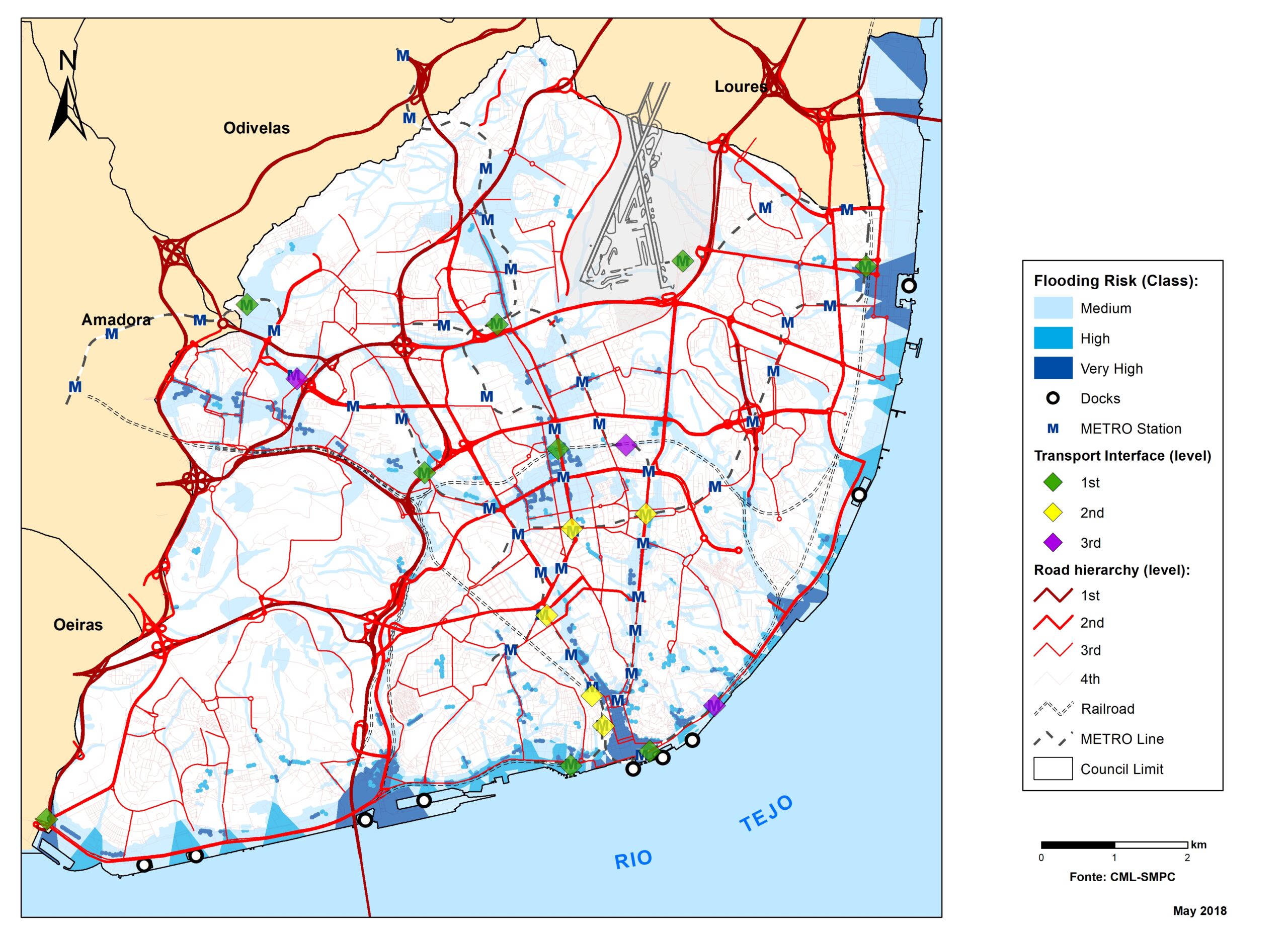
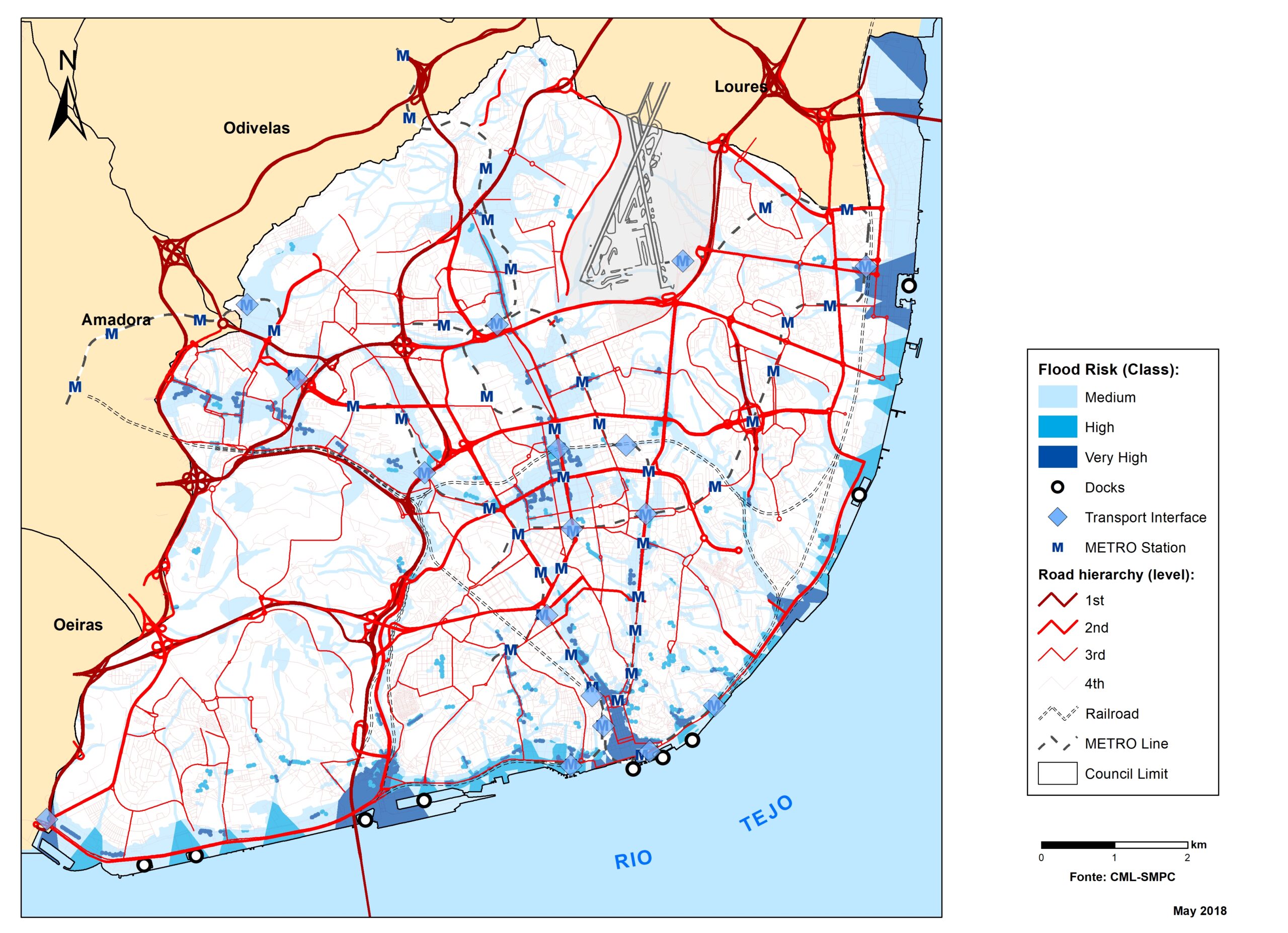
Lisbon
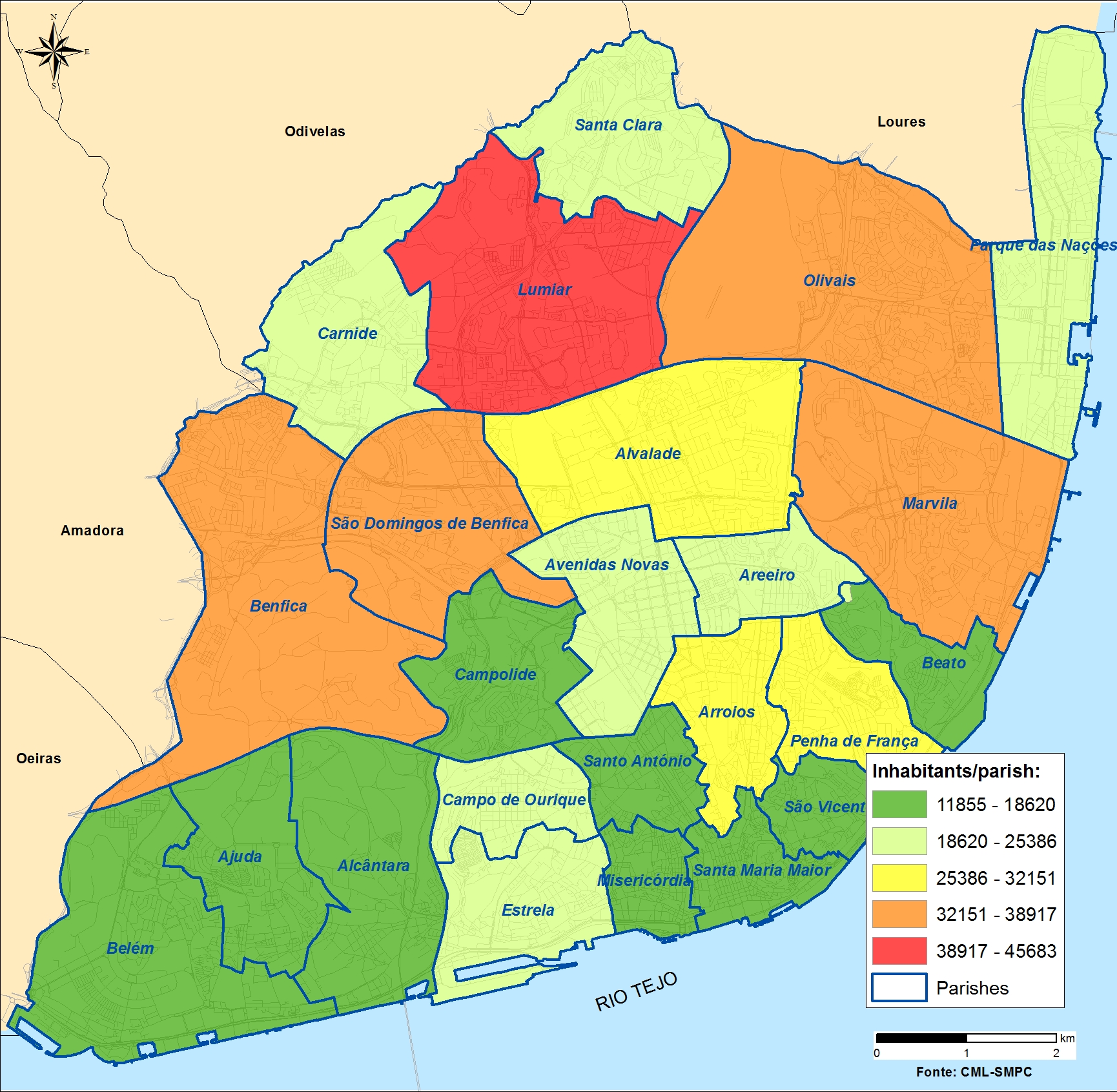
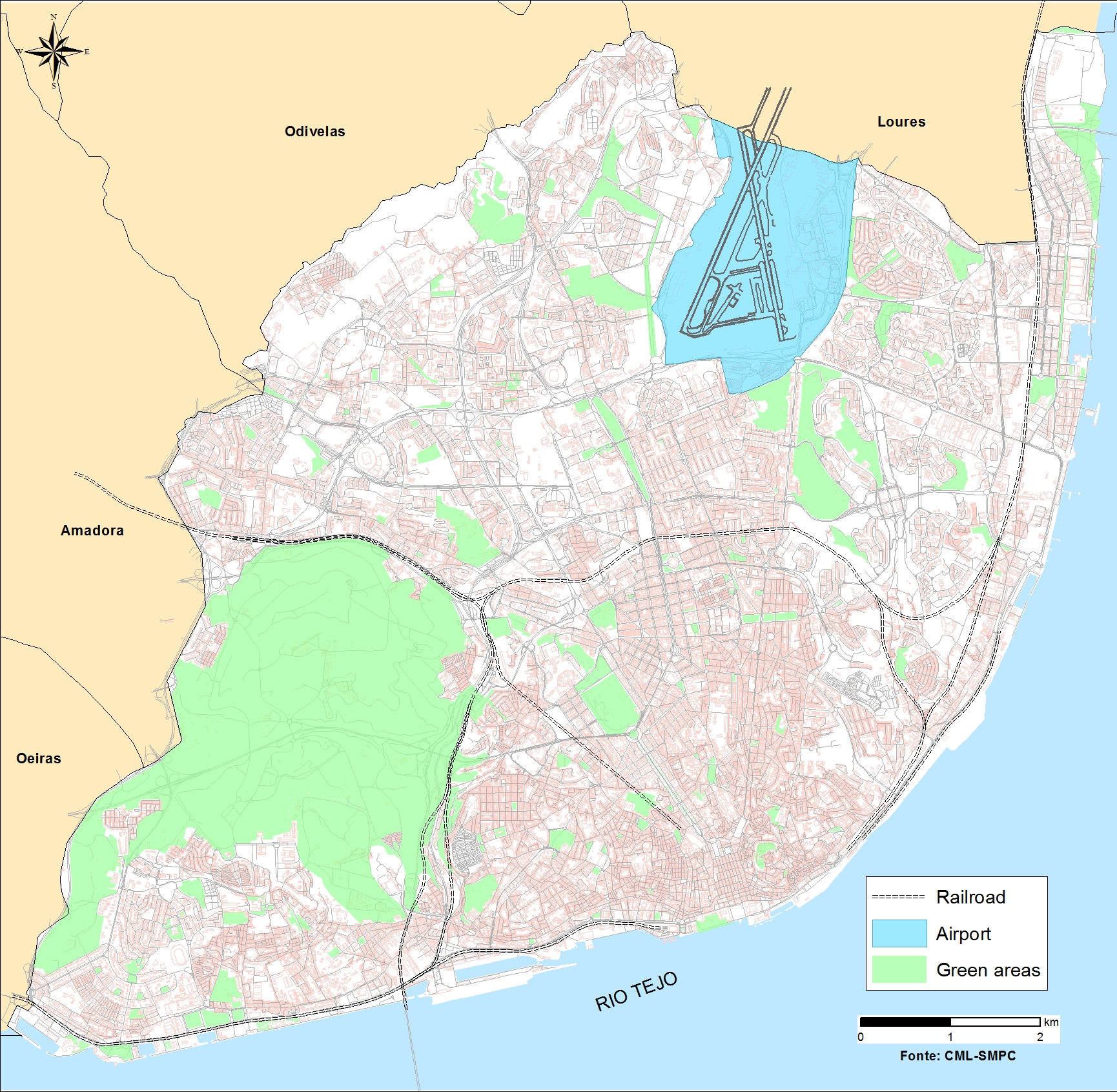
On the northern bank of the Tagus River’s estuary, the Portuguese capital is located at the middle of the Metropolitan Area with 2.8 million inhabitants. With a population of over half a million living in a complex coastal ecosystem, the city has urban challenges such as aging infrastructure, buildings, economic pressure, energy and poverty.
Lisbon has a temperate climate, classified as Mediterranean climate, and is characterised by dry and hot summers and wet and fresh winter periods. The climate change trends are average air temperature increase, decrease of annual and nonwet season rainfall, increase of wet-season rainfall and of frequency of intense rainfall events, average sea level rise, and increase of frequency of coastal floods.
Tools & Results
Publication
RAP templates & guidelines
Water-focused city resilience roadmap
+These documents support the development by any city of their resilience action plans. A template with guidance to write a Resilience Action Plan (RAP) is provided, regarding climate change, with focus on the water cycle. The city may complete or adapt the template suggestions to fit better its own context and expectations for this document.
Publication
Resilience Action Plan of Lisbon
Water-focused city resilience roadmap
+It is a document containing the resilience action plan for each city defining the roadmap for resilience enhancement, to climate change with focus on water. It includes the information on the work already existing in the city, definition of climatic scenarios, characterization of the context, and hazards, risk and resilience assessment, description and implementation planning of strategies to be implemented to improve resilience. It is a thematic plan that can contribute to the city’s global resilience plan and it was built based on RESCCUE’s template and guidelines and on the results obtained, using the tools and approaches developed in RESCCUE.
Tool
RESCCUE Assessment Framework tool for application
Water-focused city resilience roadmap
+RESCCUE RAF-APP is a tool to facilitate undertaking a structured urban resilience assessment to climate change providing easy visualization of results through graphical representation. The tool enables assessing the development level of city resilience, considering strategic services and interdependencies contributions to city resilience. Services included are water supply, wastewater, storm water and waste management, energy distribution and mobility. It also supports to assess resilience development level of the service. This allows identifying the main strengths and weaknesses in the city and services. Its main purpose is to support decision in the development of resilience action plans and assess progress.
Registration is required to use the RAF APP. Please contact macardoso@lnec.pt.
Methodology
Framework for the Resilience Action Plan
Water-focused city resilience roadmap
+It is an approach that provides a planning process by defining the main steps to follow to develop resilience action plans, It includes the information needed to produce an action plan for enhancing resilience of any city, based on the work already existing in the city, the definition of climatic scenarios, characterization of the context and hazards, risk and resilience assessment and development of strategies to be implemented to improve resilience.
More information:
Methodology
Framework for cities resilience assessment
Water-focused city resilience roadmap
+RESCCUE RAF is a framework that provides a structured system for urban resilience assessment to climate change, considering four dimensions: organisational integrating top-down governance relations and urban population involvement; spatial referring to urban space and environment; functional regarding strategic services’ resilience and physical looking at infrastructures’ resilience. It is objective-driven enabling to assess the development level of city resilience, considering strategic services and interdependencies contributions to city resilience. Services included are water supply, wastewater, storm water and waste management, electrical energy and mobility. Its main purpose is to support decision in the development of resilience action plans and assess progress.
More information:
Dataset
Tool and database for the selection of adaptation strategies
Resilience & adaptation strategies
+A prioritization methodology has been developed to rank the proposed climate adaptation measures. This methodology will assist to decision makers to select the most efficient measures in terms of both their costs and the degree of risk reduction that they can guarantee. Besides, the methodology has been integrated into a web-based platform that will assist the decision makers to conduct the process of prioritization. The platform includes an extensive database of adaptation measures gathered by the different project partners based on their experience in the three cities that act as case studies in the project (Barcelona, Bristol and Lisbon)
Publication
Assessment of city resilience in Lisbon
Holistic resilience assessment & management
+This video presents the main steps of RESCCUE methodology application in Lisbon Research Site. From the identification of resilience-related goals, key stakeholders to engage and critical services and infrastructures to include in the analysis; to the study of interdependencies and consequent cascade effects triggered by a climate-related disruptive even, in the case, rainfall induced floods. In Lisbon, 19 services from 7 sectors were considered, including 146 infrastructures. Data collection was performed through a set of 13 meetings, at the service operational level, and 5 local workshops, at strategic and steering levels, involving all the key stakeholders.
Dataset
Flood direct damage assessments
Impact assessment & cascading effects
+The Direct Damage Assessment data for the Bristol case study is derived via the analysing water depths that are in contact with buildings to estimate the damages based on the building use and the associated depth-damage relationship. The functions for Bristol are obtained from the Multi-colour Manual (MCM ). The MCM contains information derived from historical insurance data that relates damage estimates to properties based on surrounding flood depth and said properties land use classification. The dataset herein presented outlines the aggregated damages to flooded buildings based on their exposure to flood waters and their respective depth-damage curves.
Publication
Impact quantification indices in the electrical network
Impact assessment & cascading effects
+GIS-based methodology designed for the assessment of electrical substations and distribution centres in case of extreme flooding events and extensible to other climate extreme events such as earthquakes, heat waves, and extreme windstorms if electric poles are also included into the assessment. This methodology has been thoroughly explained in “Electrical Grid Risk Assessment Against Flooding in Barcelona and Bristol Cities” paper.
Dataset
Assessment of marine model impacts
Strategic urban services modelling
+Integrated urban drainage – marine model provided temporal and spatial evolution of pollution in receiving bathing water. Dataset is built with time series of rainfall, CSO discharges and pollution in representative points of bathing water during the characteristic bathing season of the year 2009.
Dataset
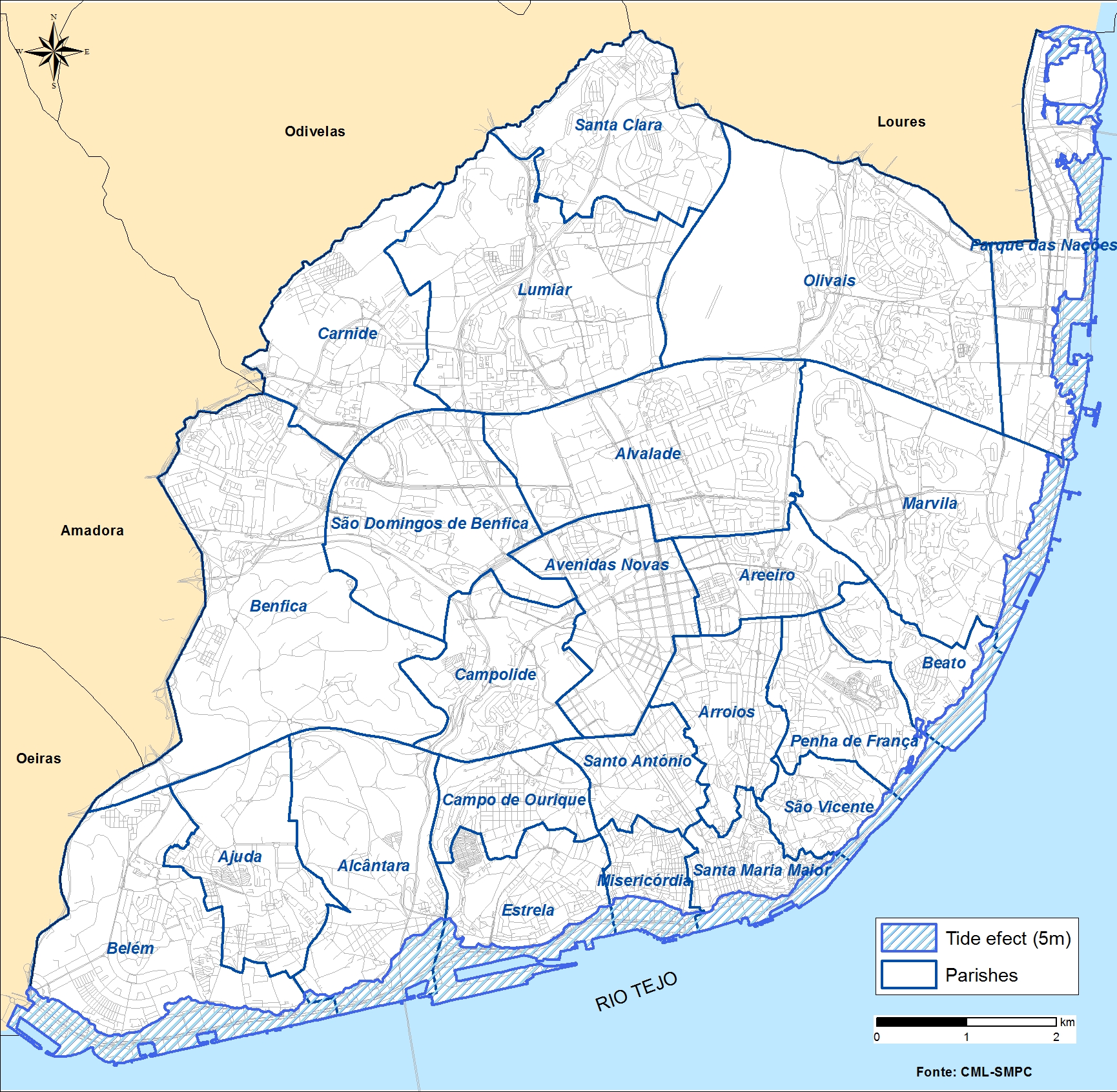
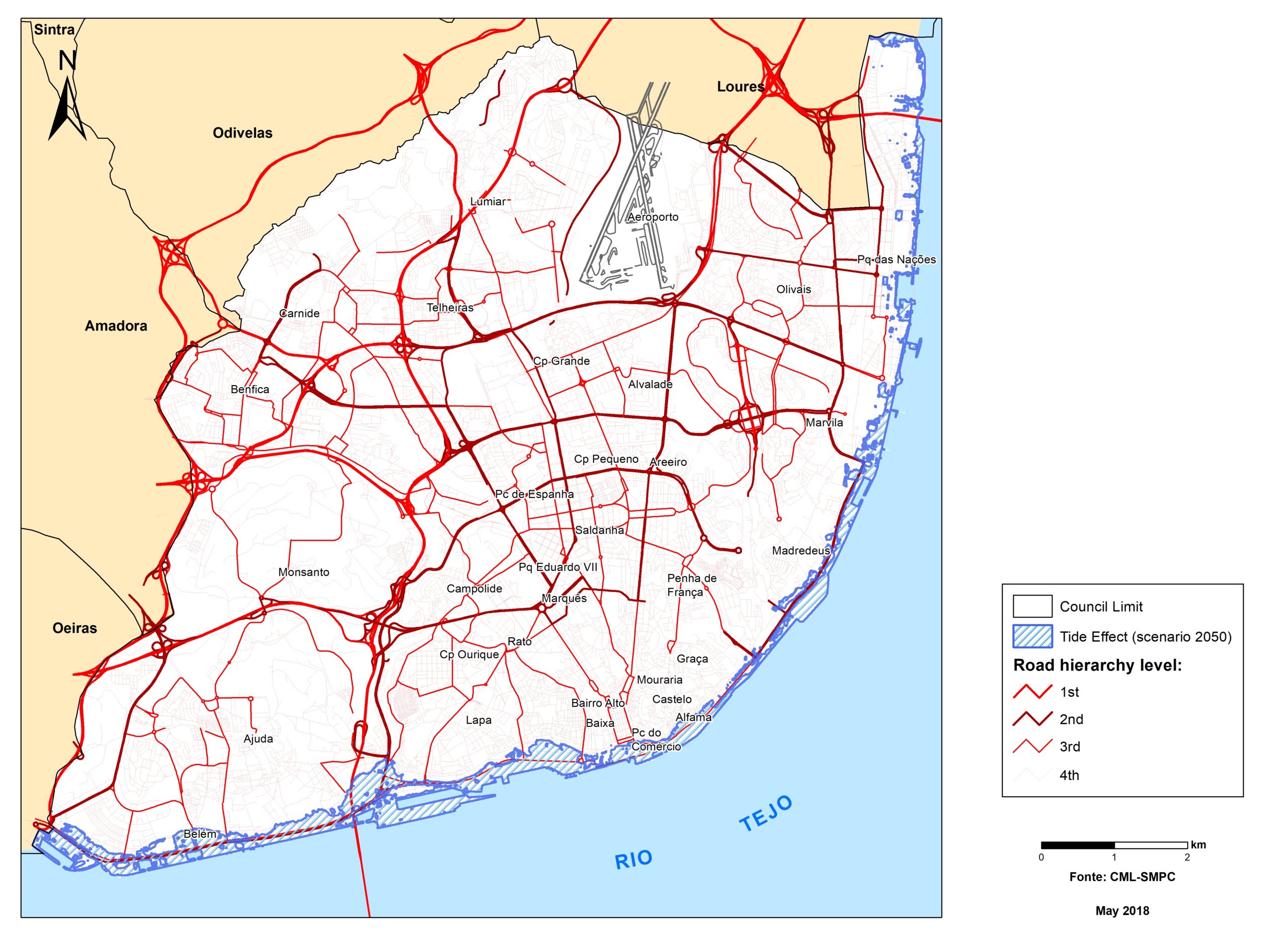
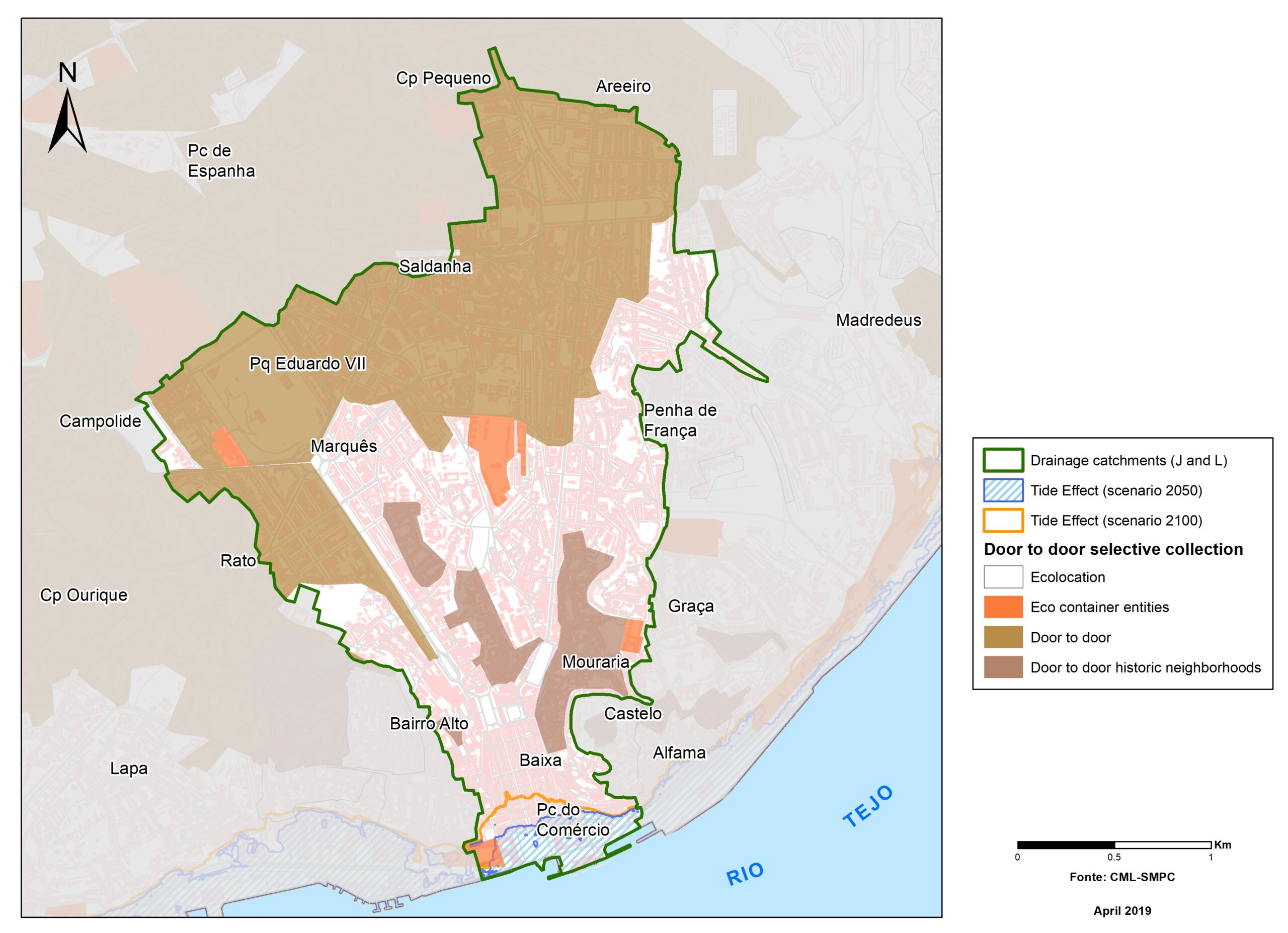
Sea level rise impact model
Strategic urban services modelling
+Critical infrastructures and services potentially exposed to sea level rise for the horizon of 2100 have been represented by exposure maps for RCPs 4.5 and 8.5 scenarios.
Dataset
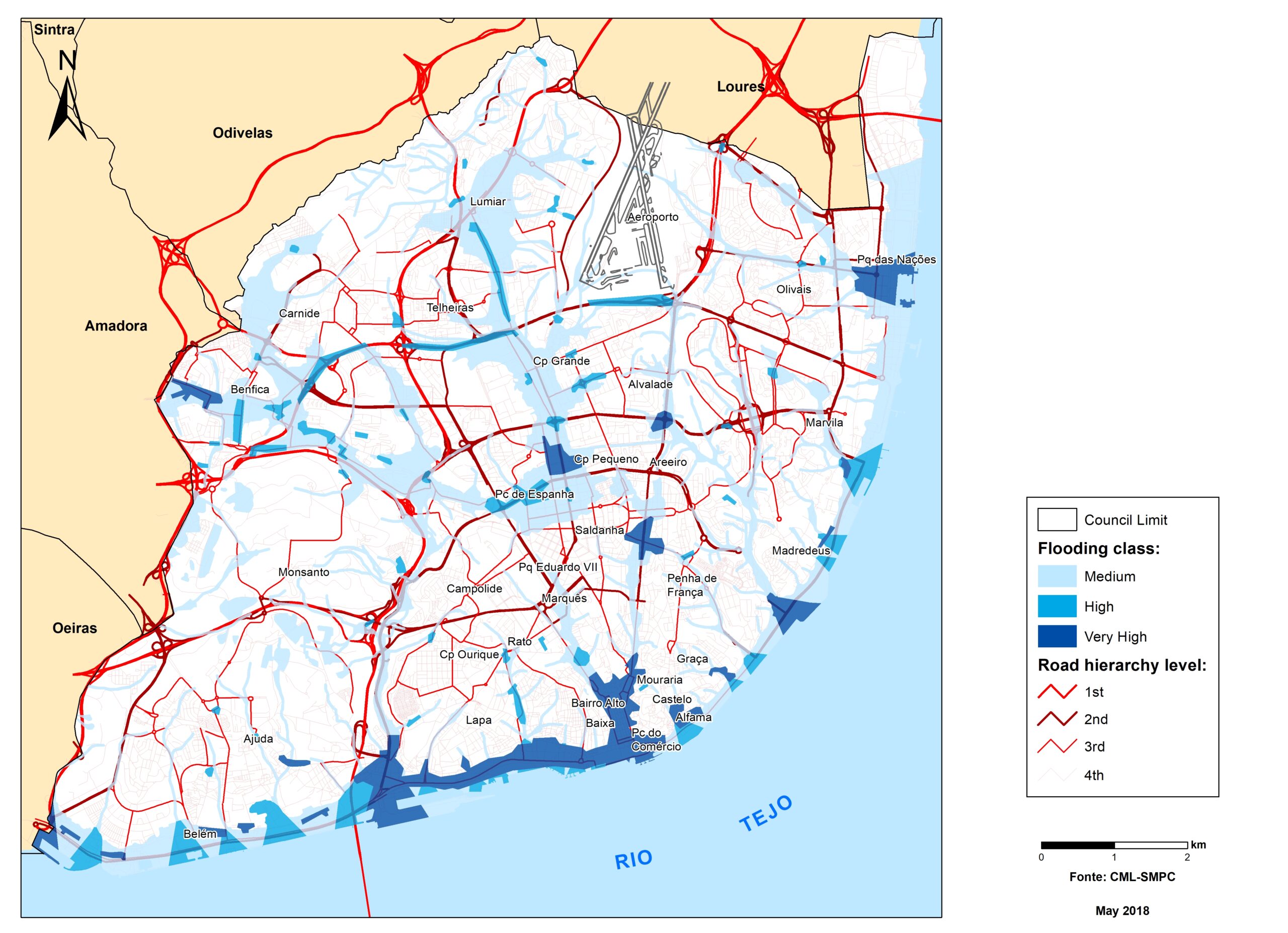
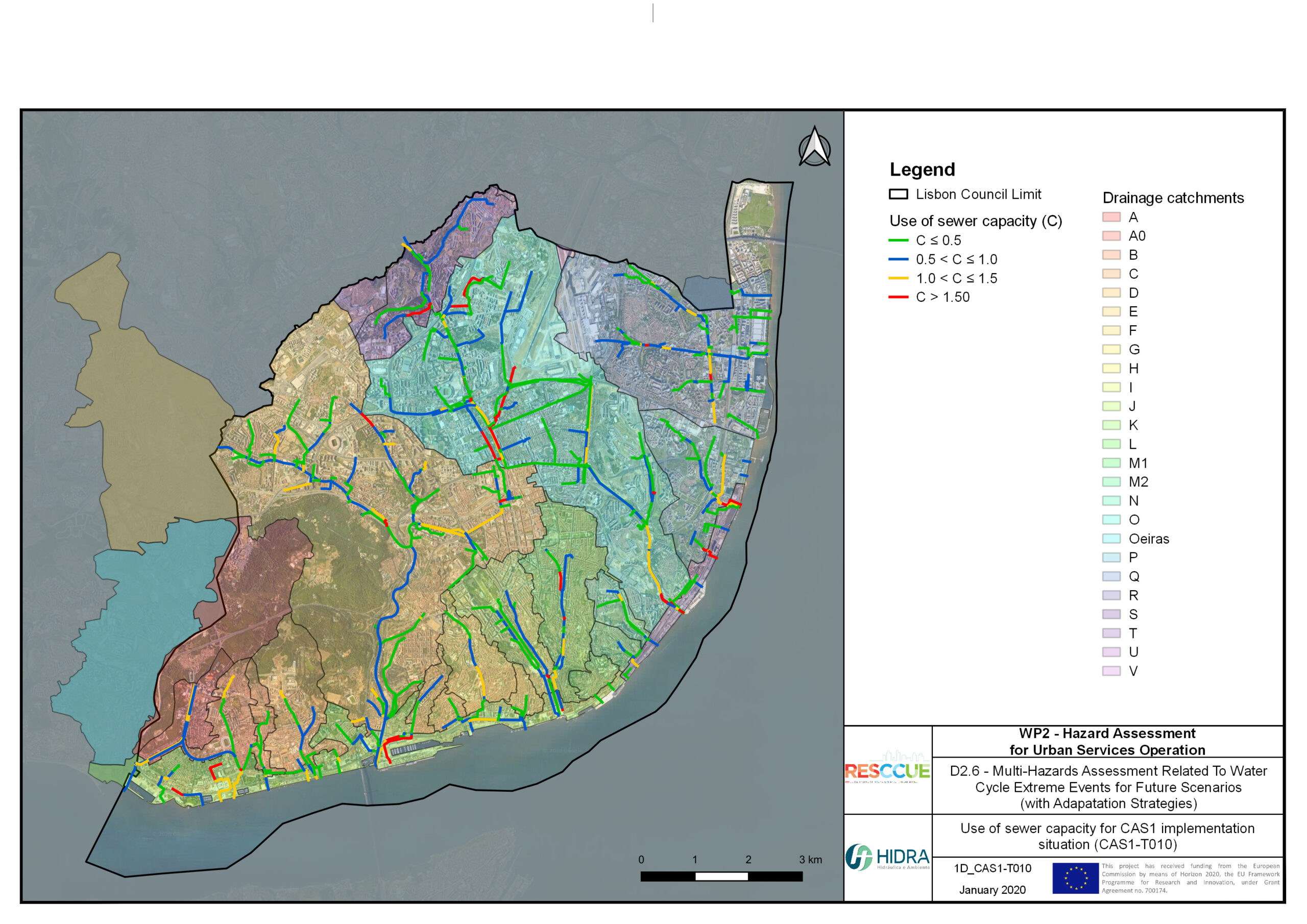
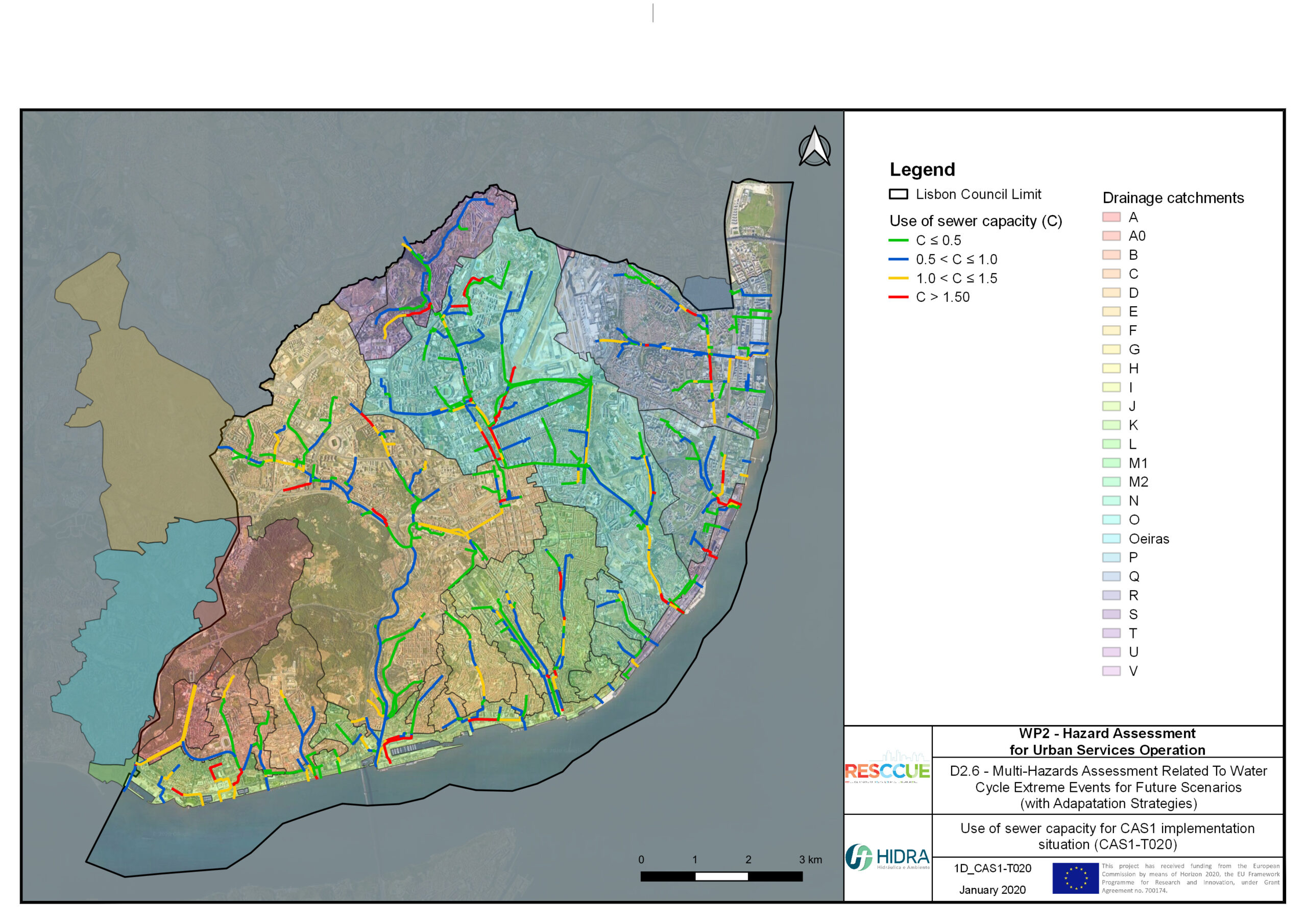
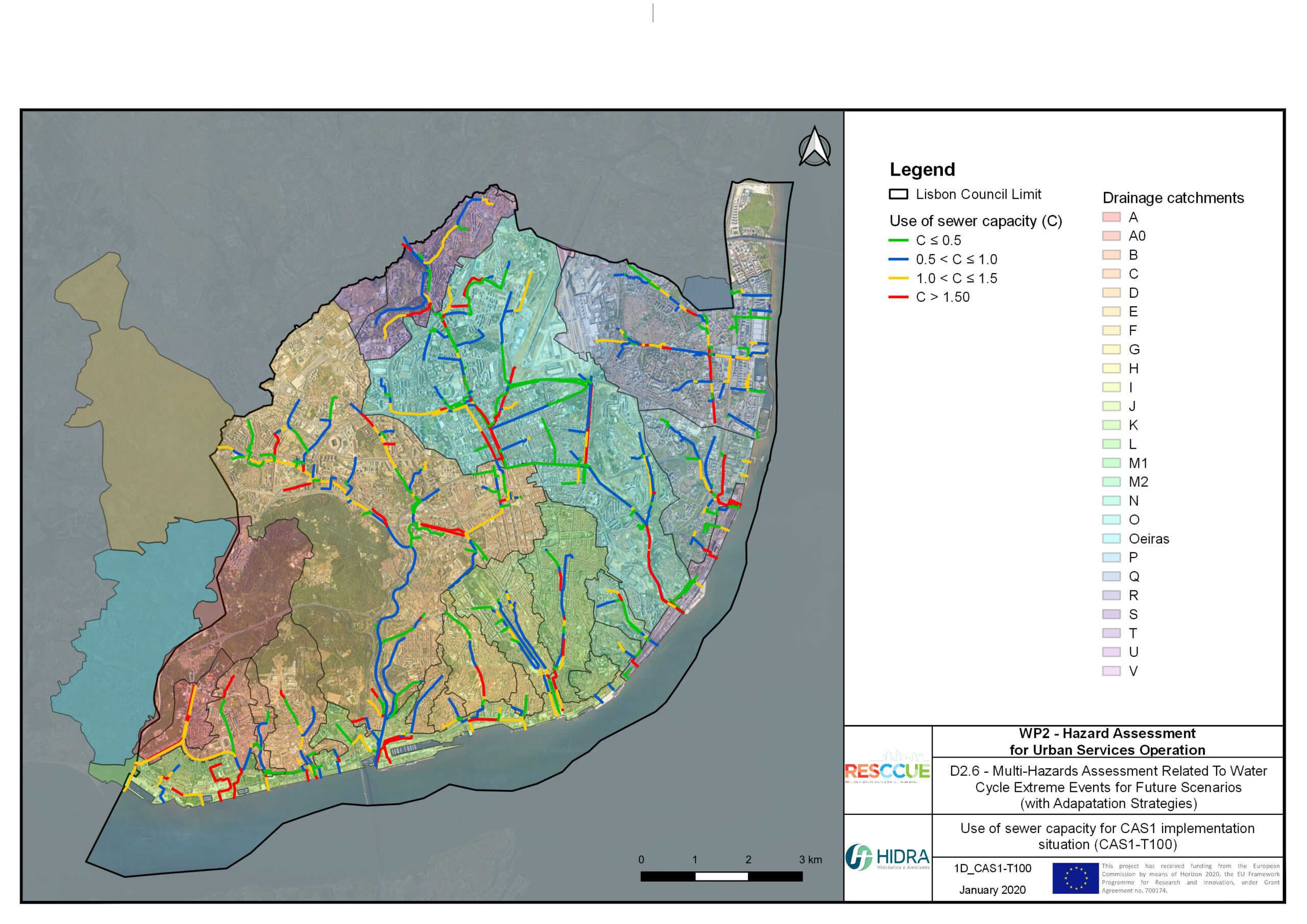
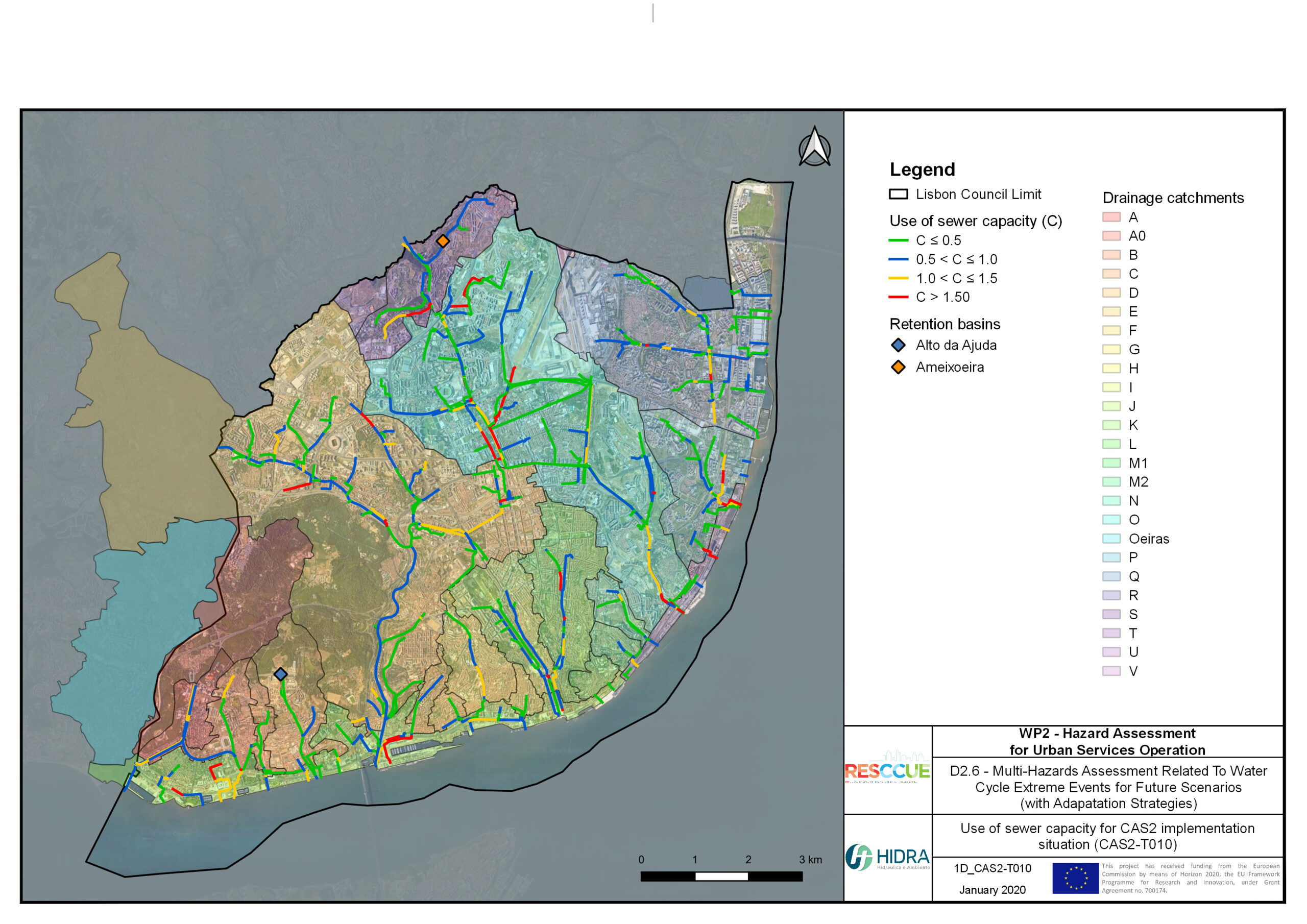
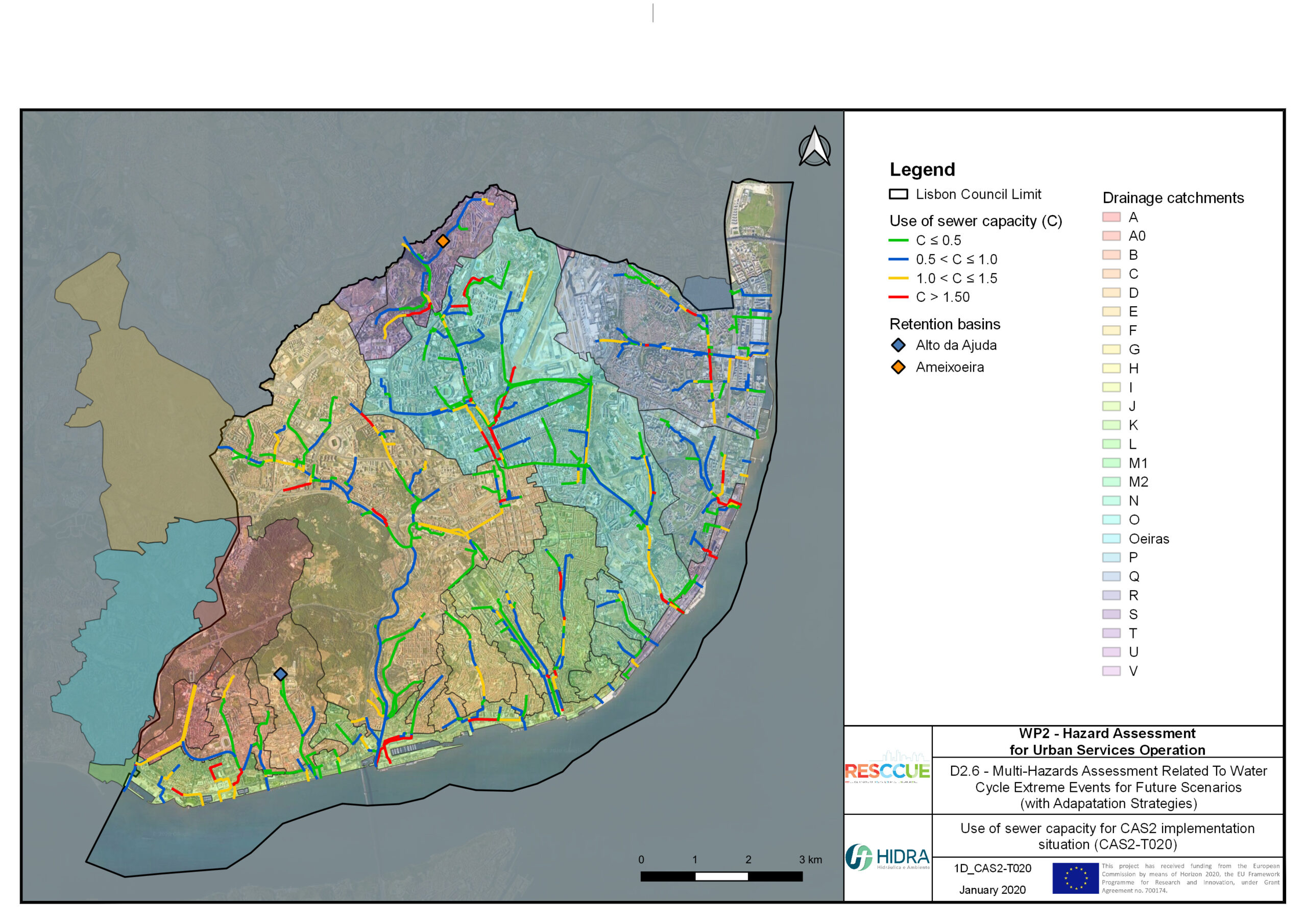
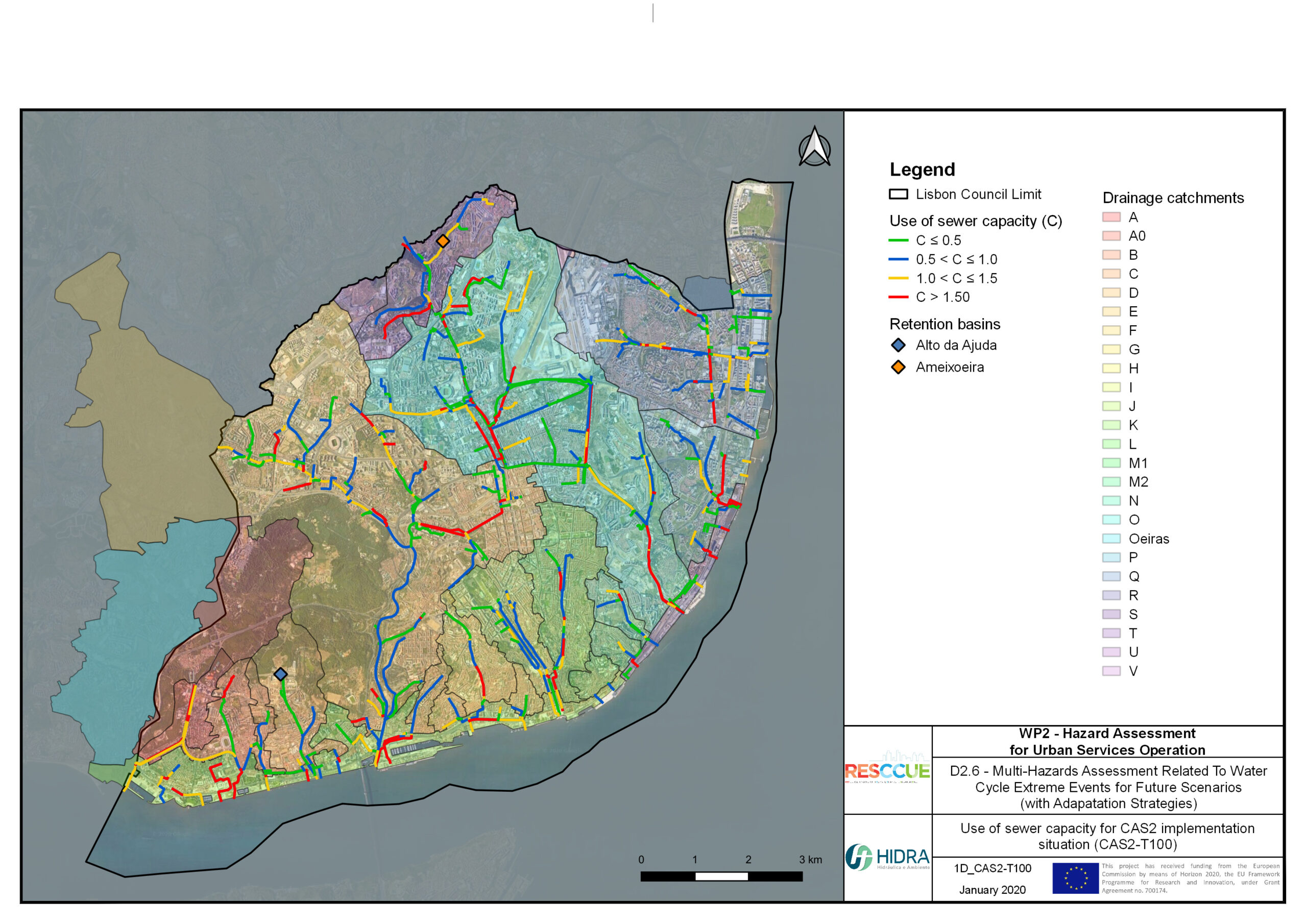
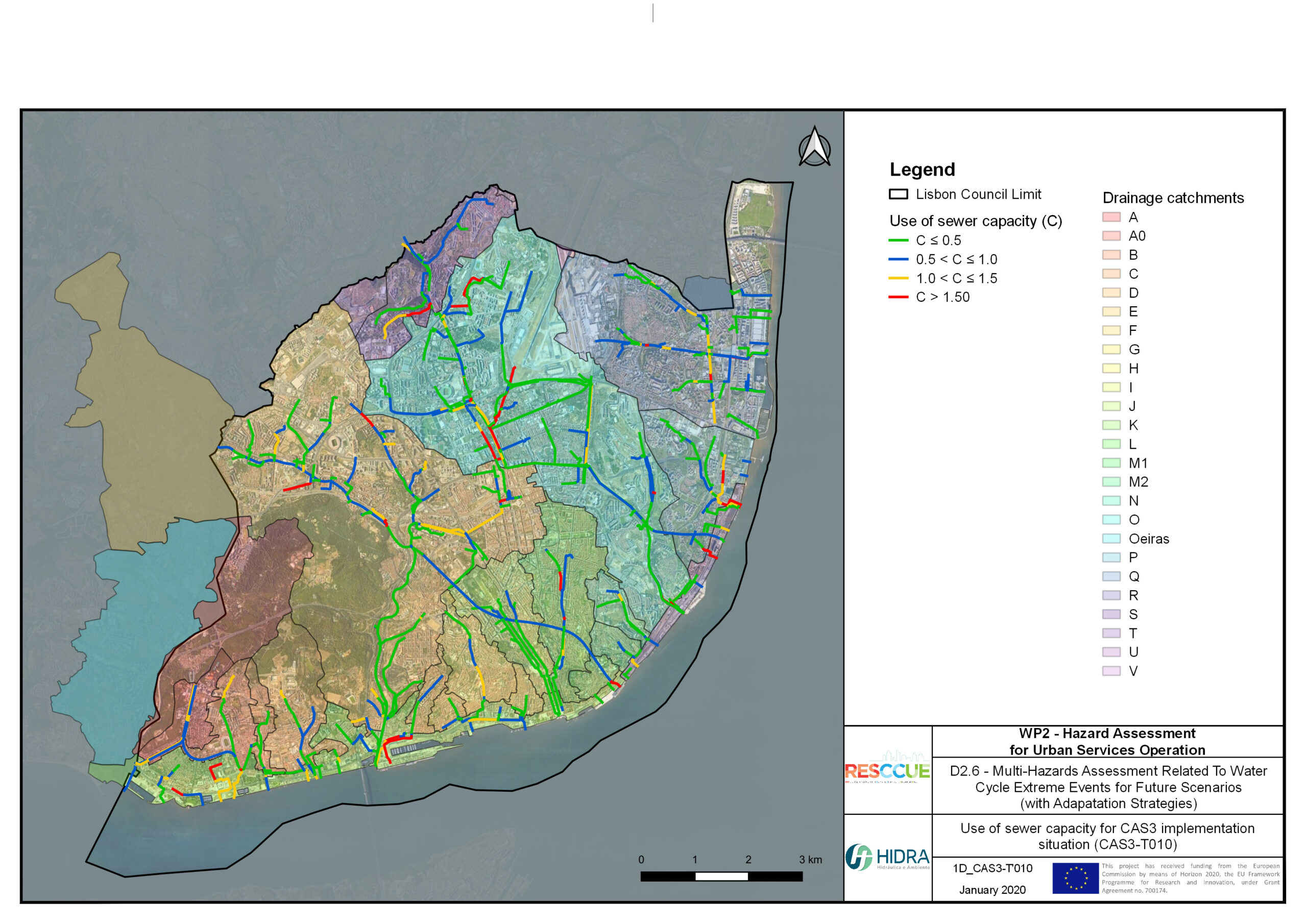
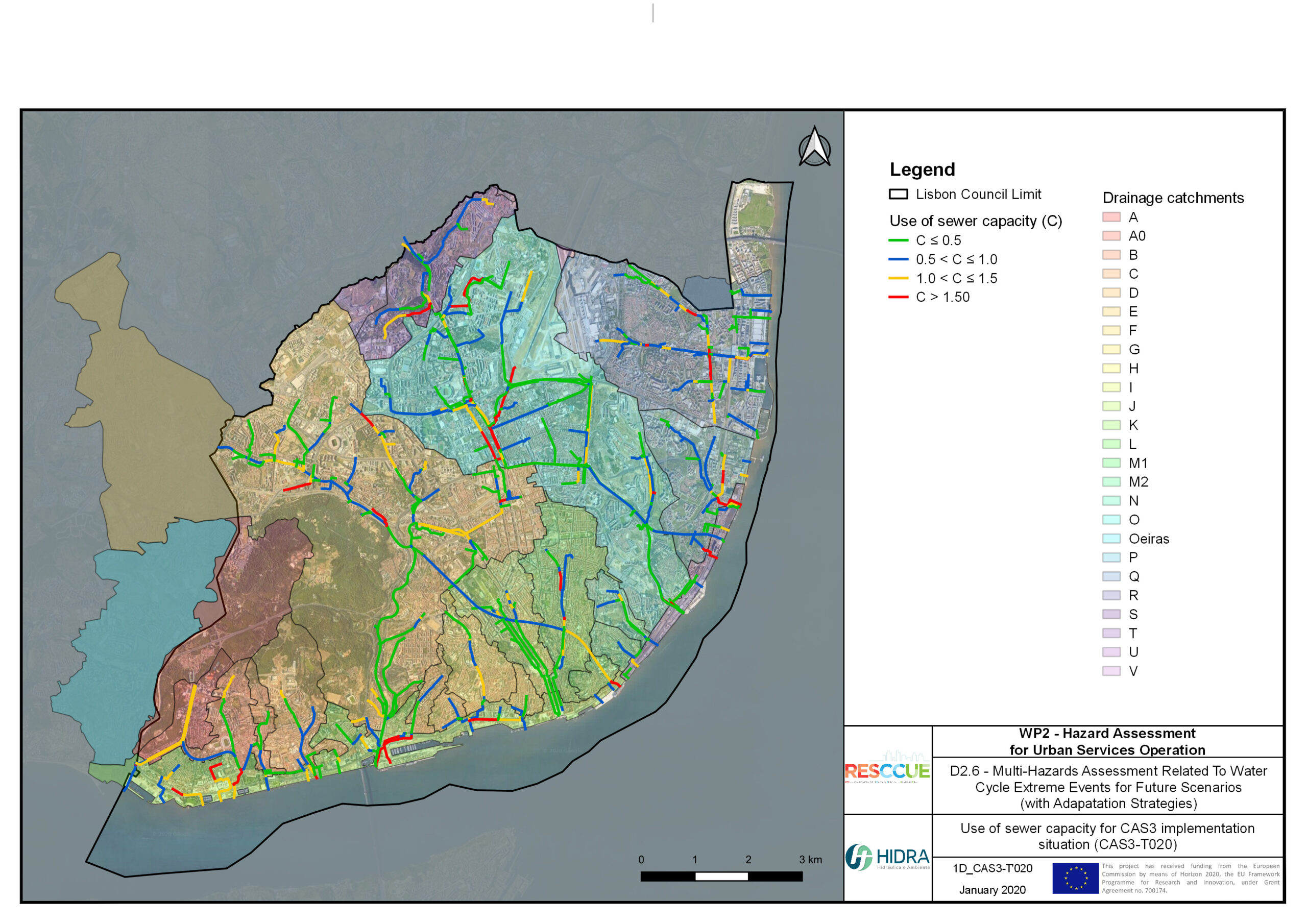
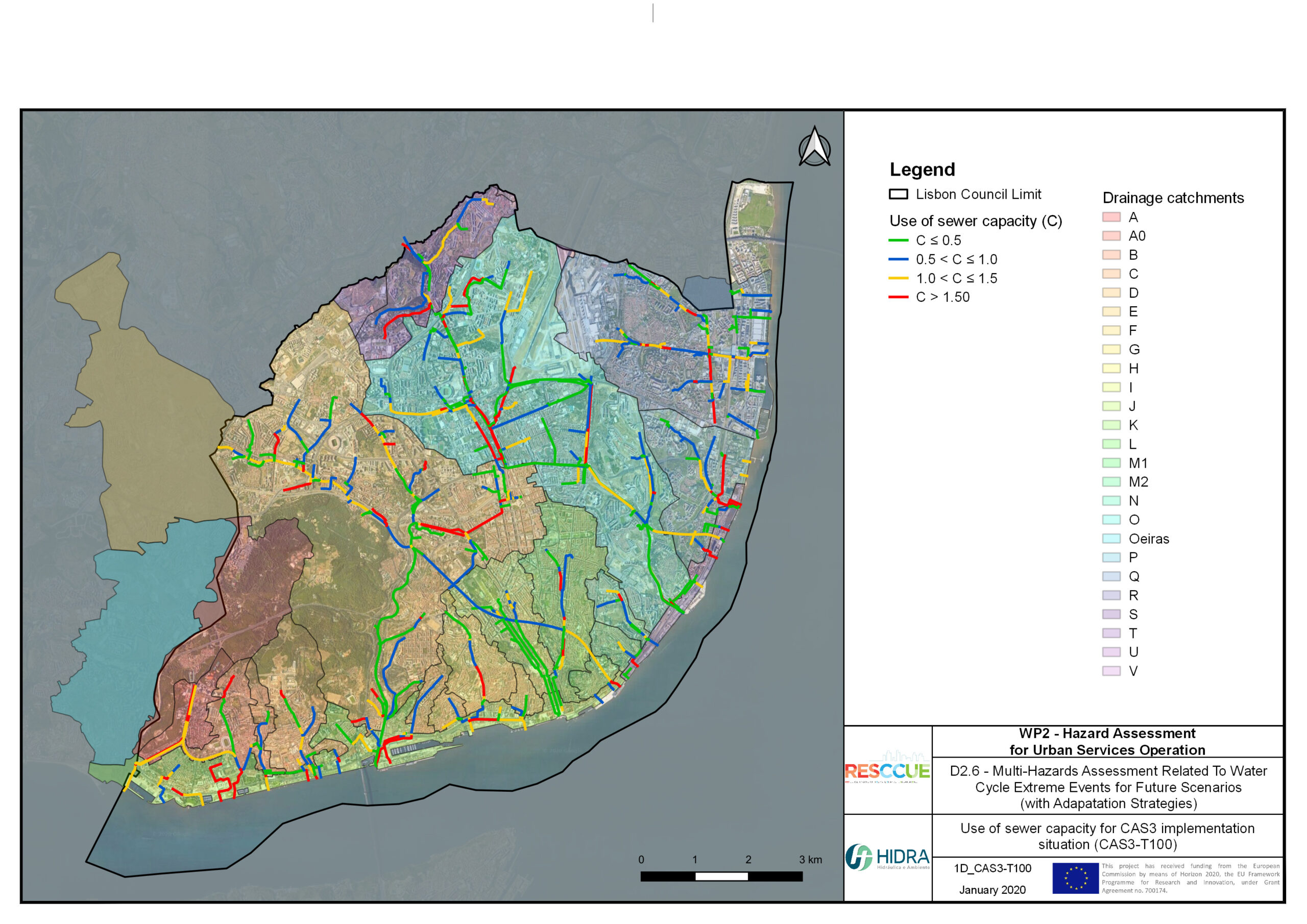
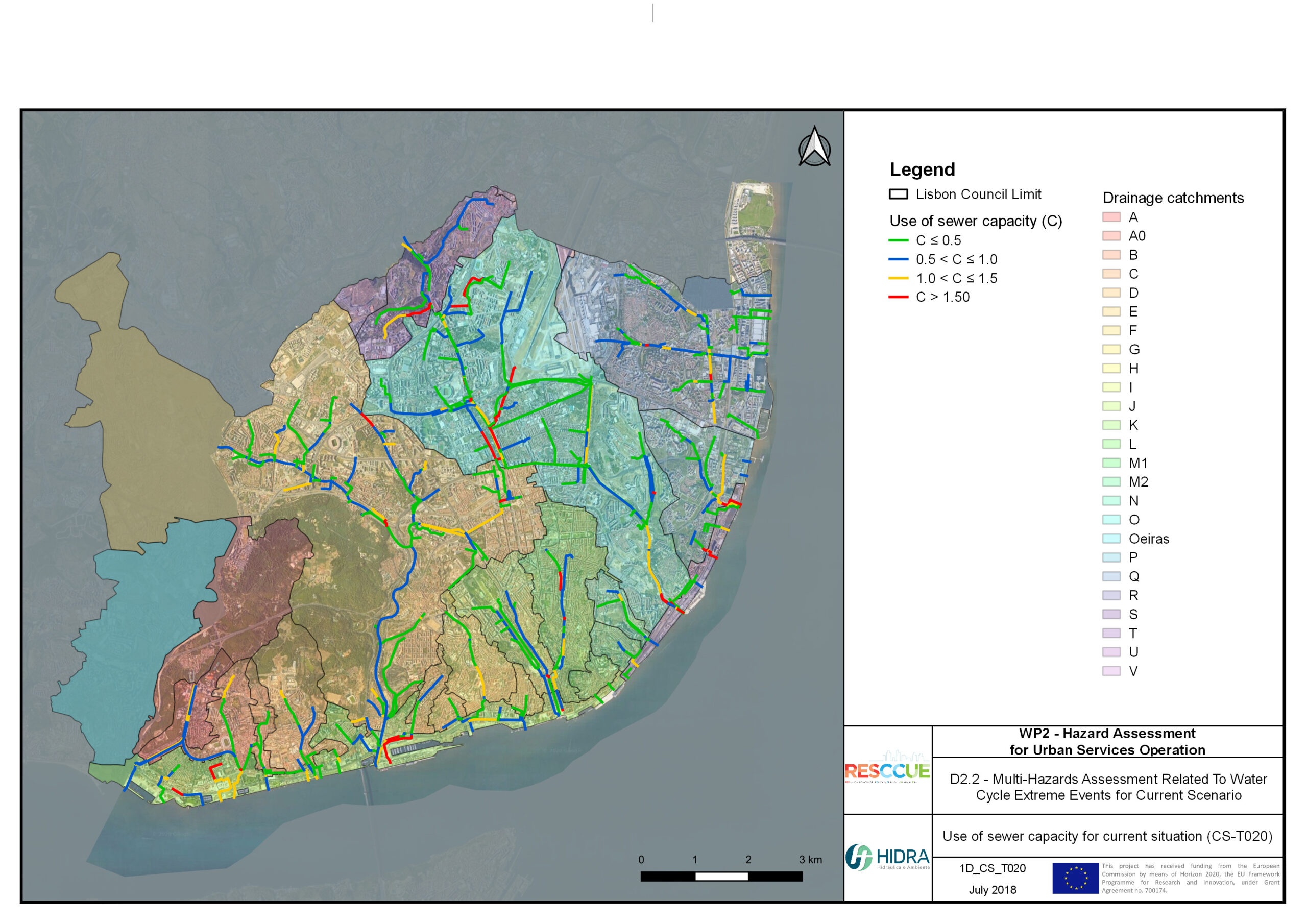
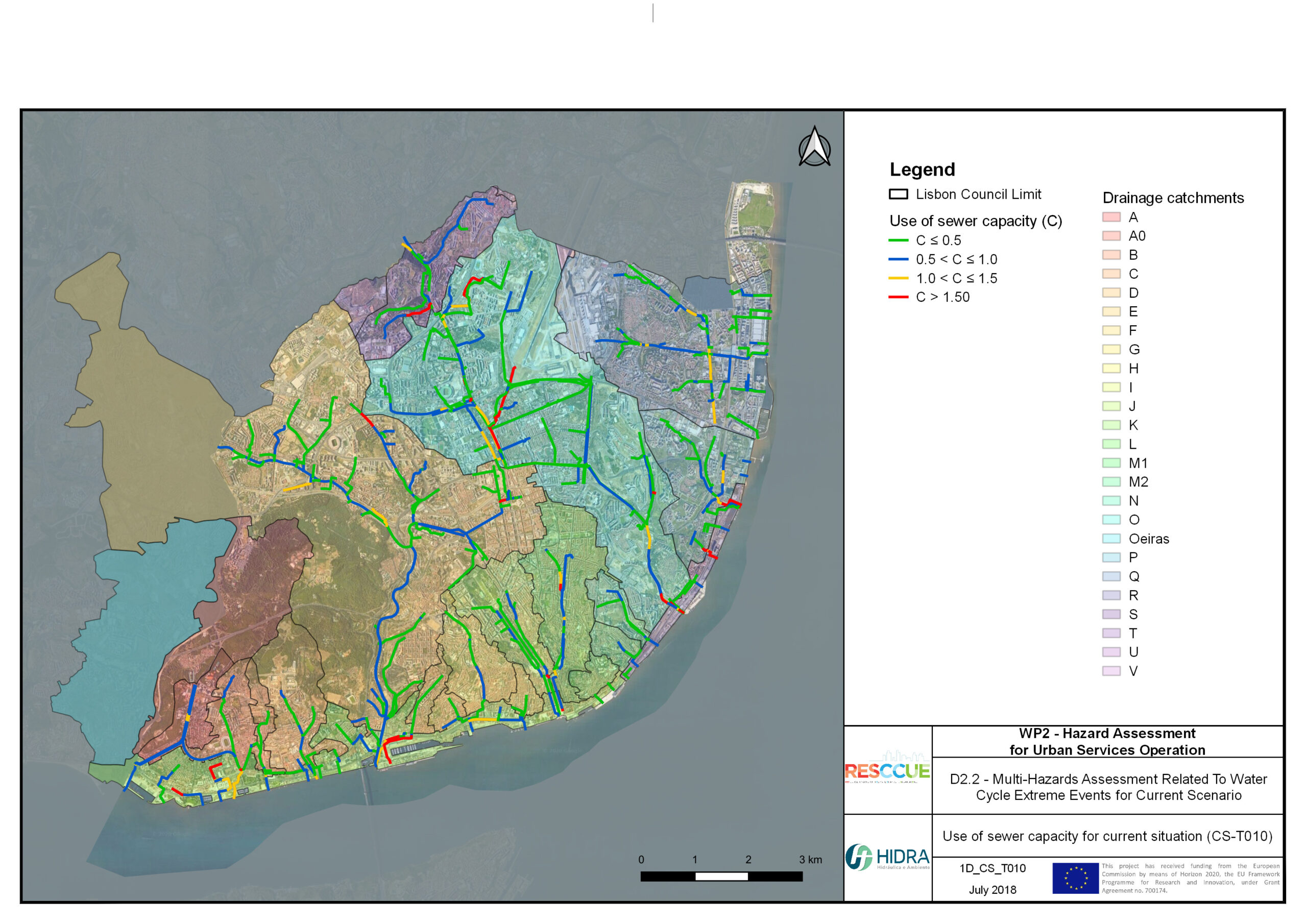
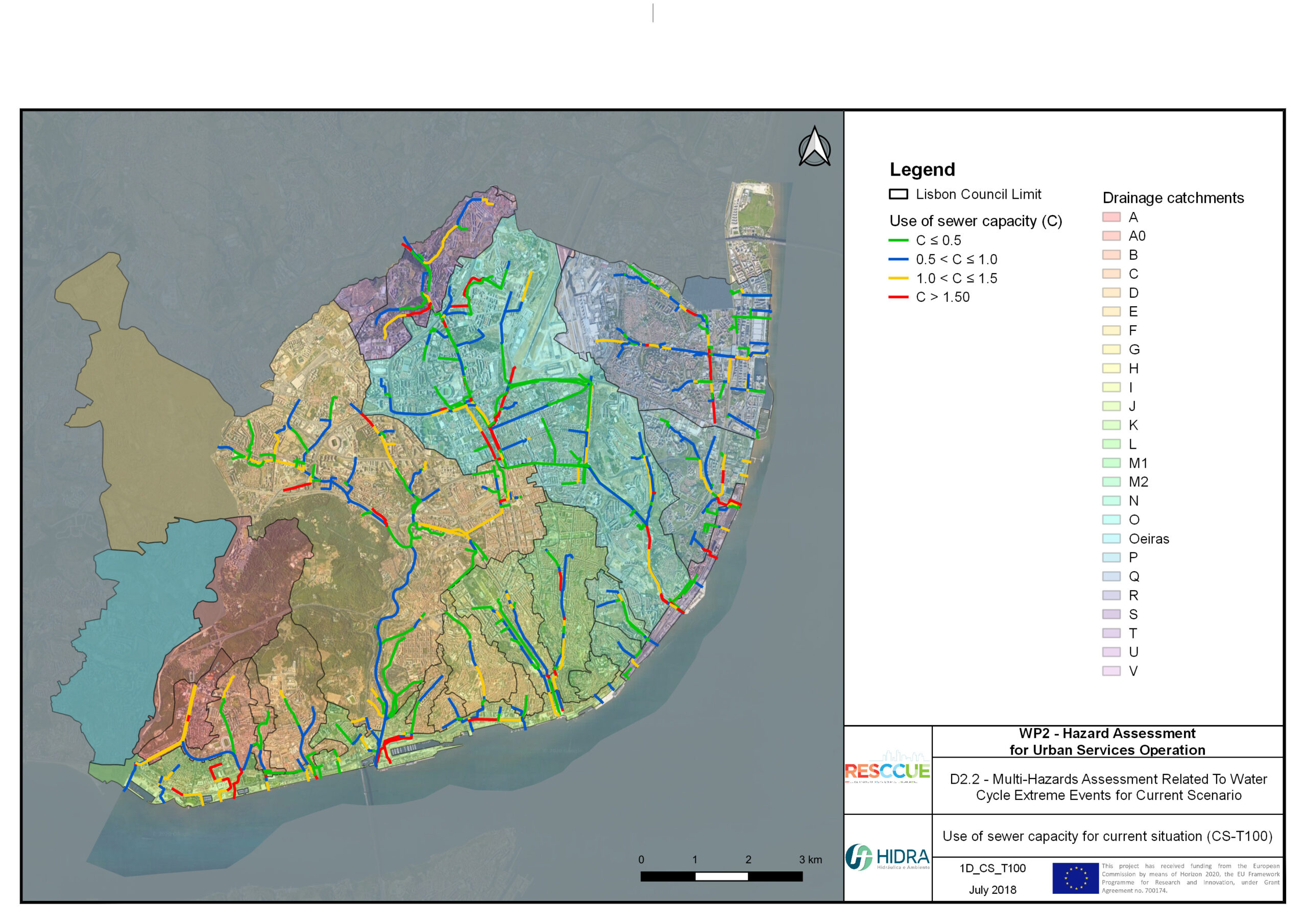
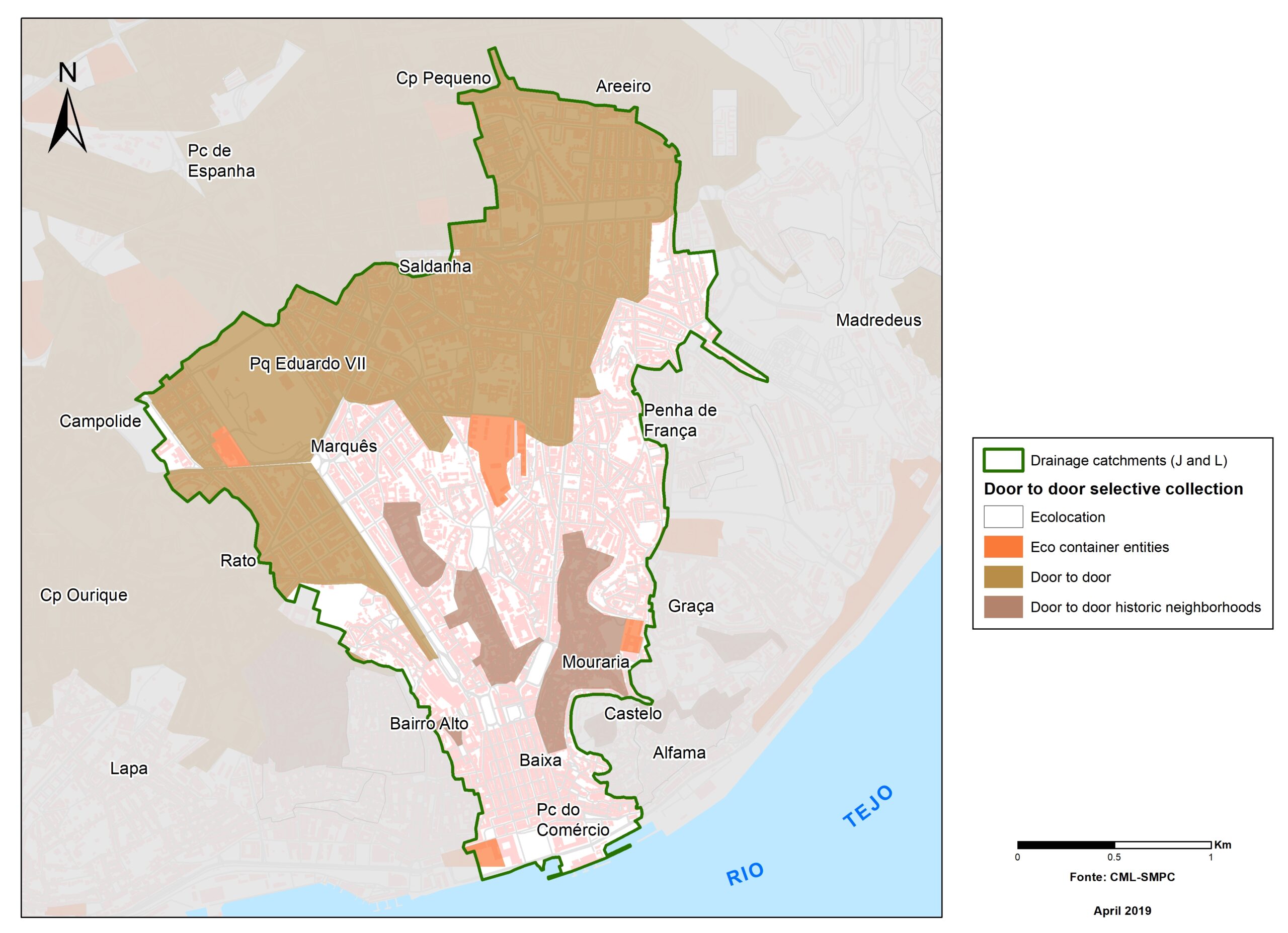
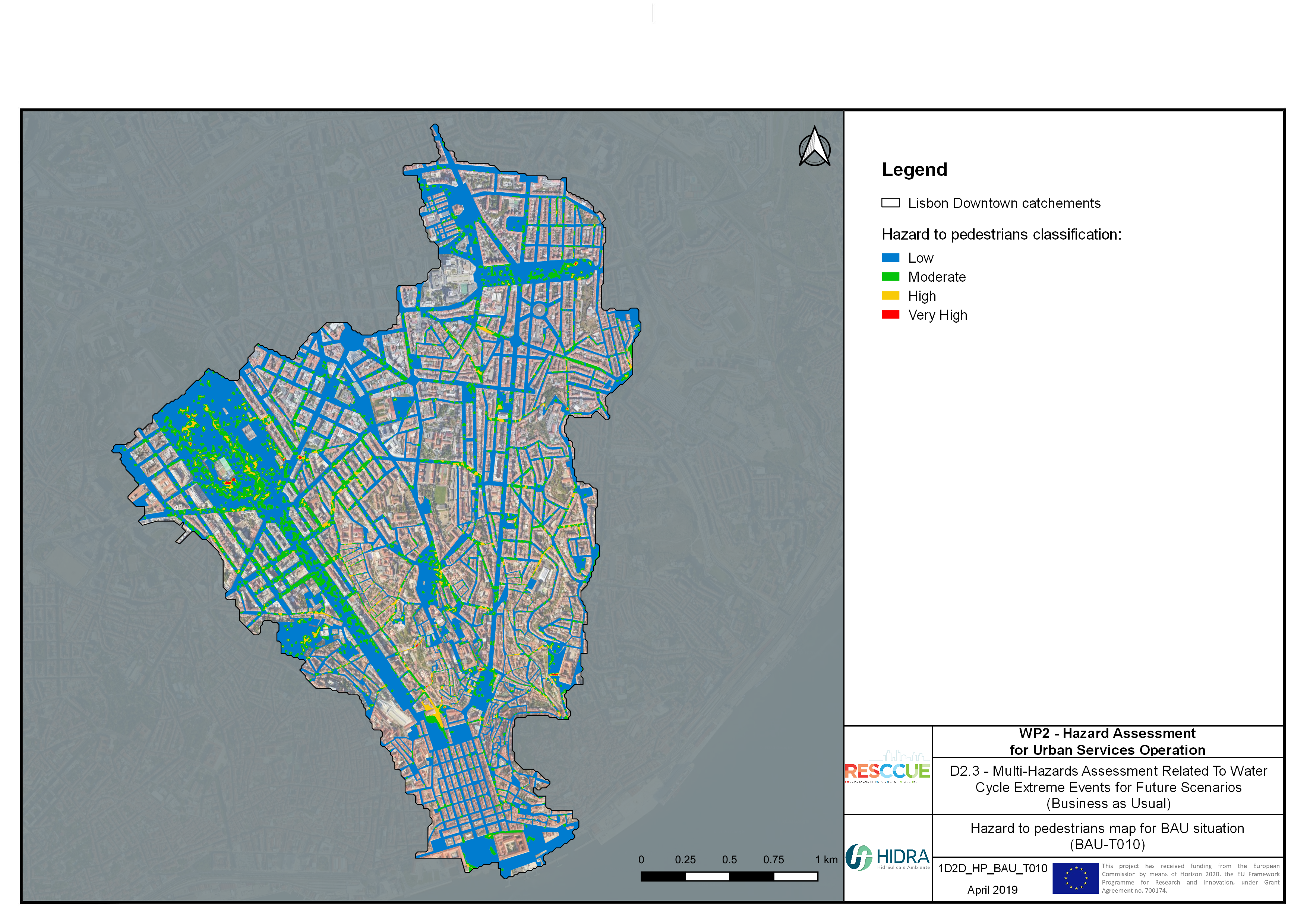
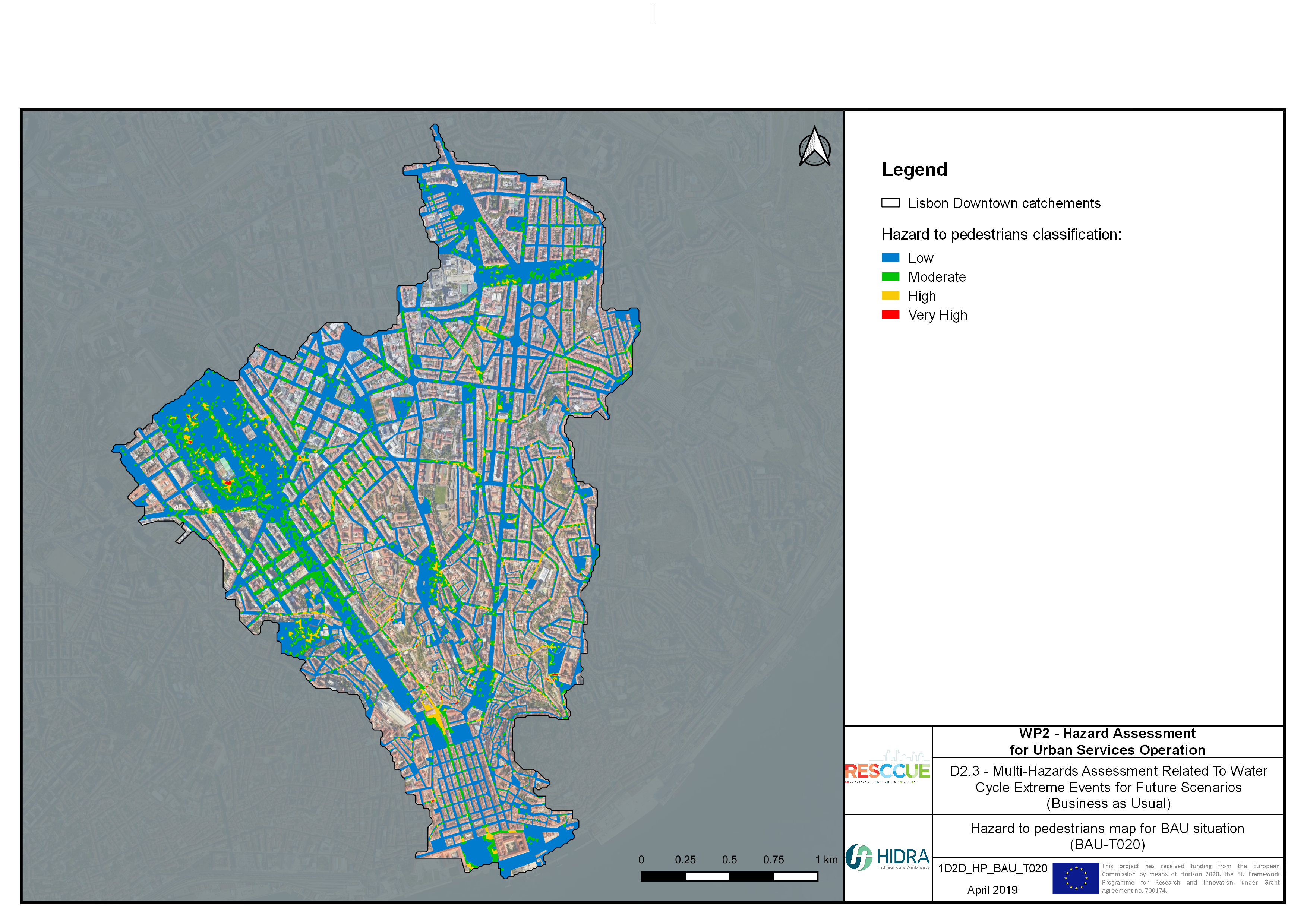
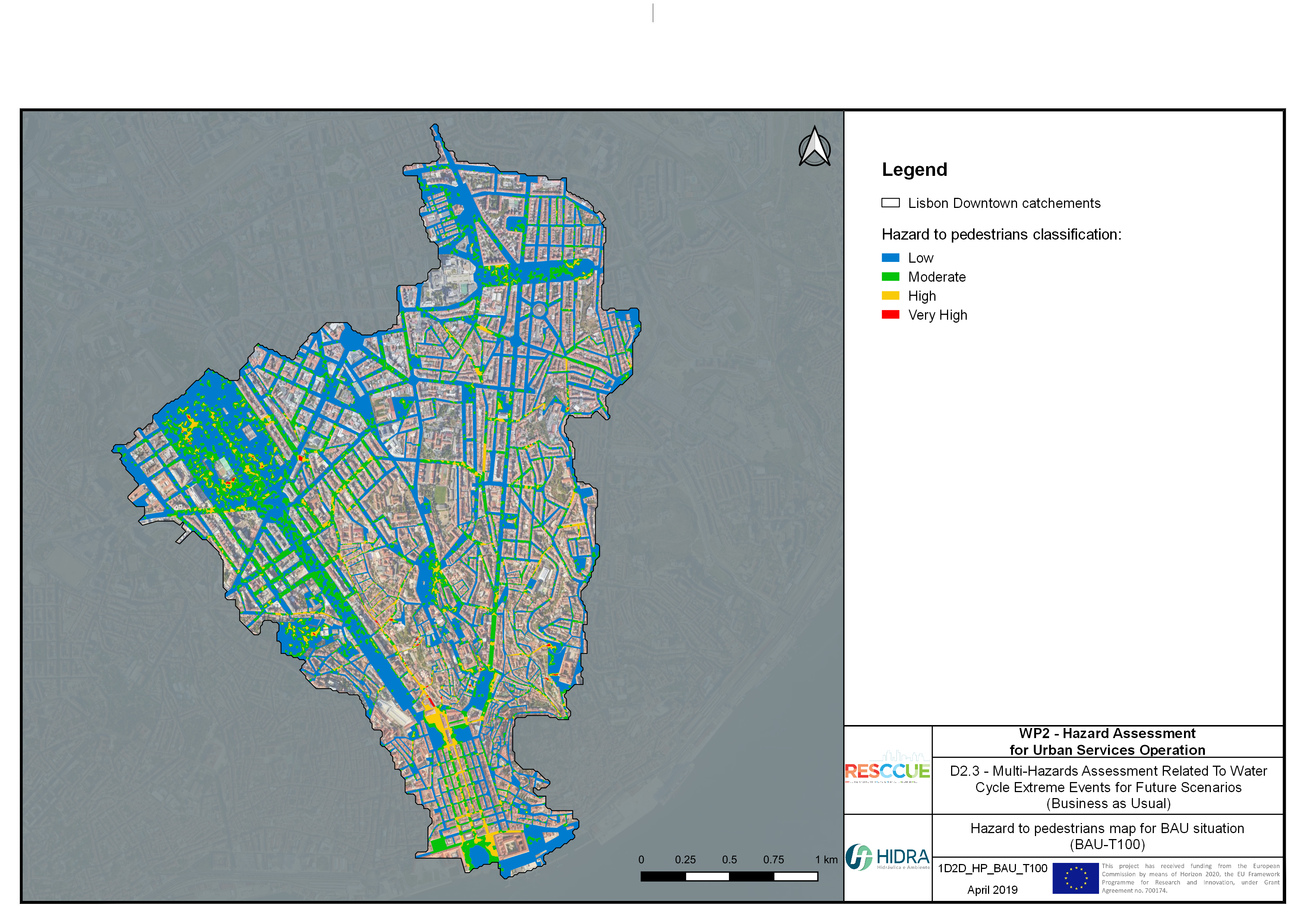
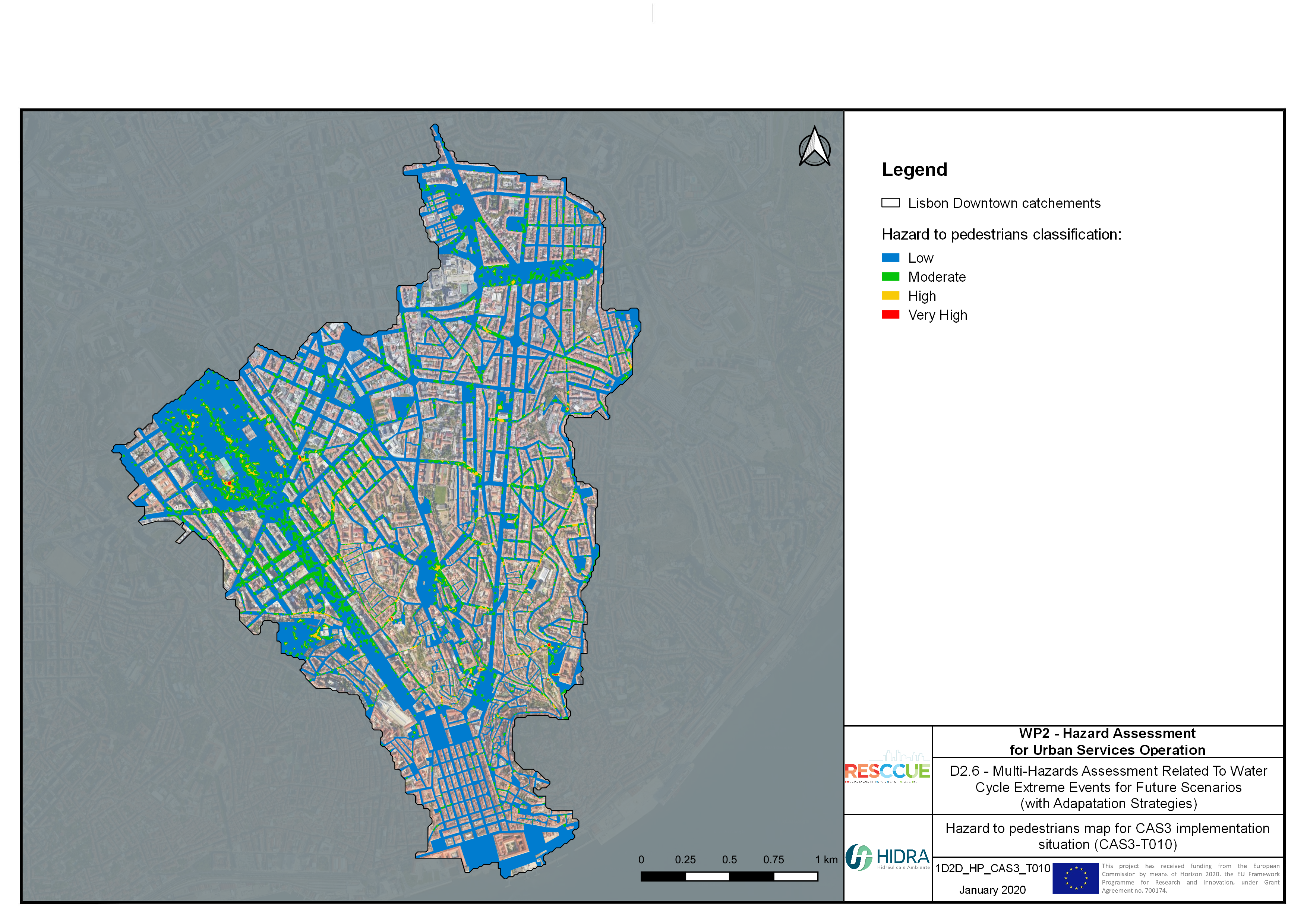
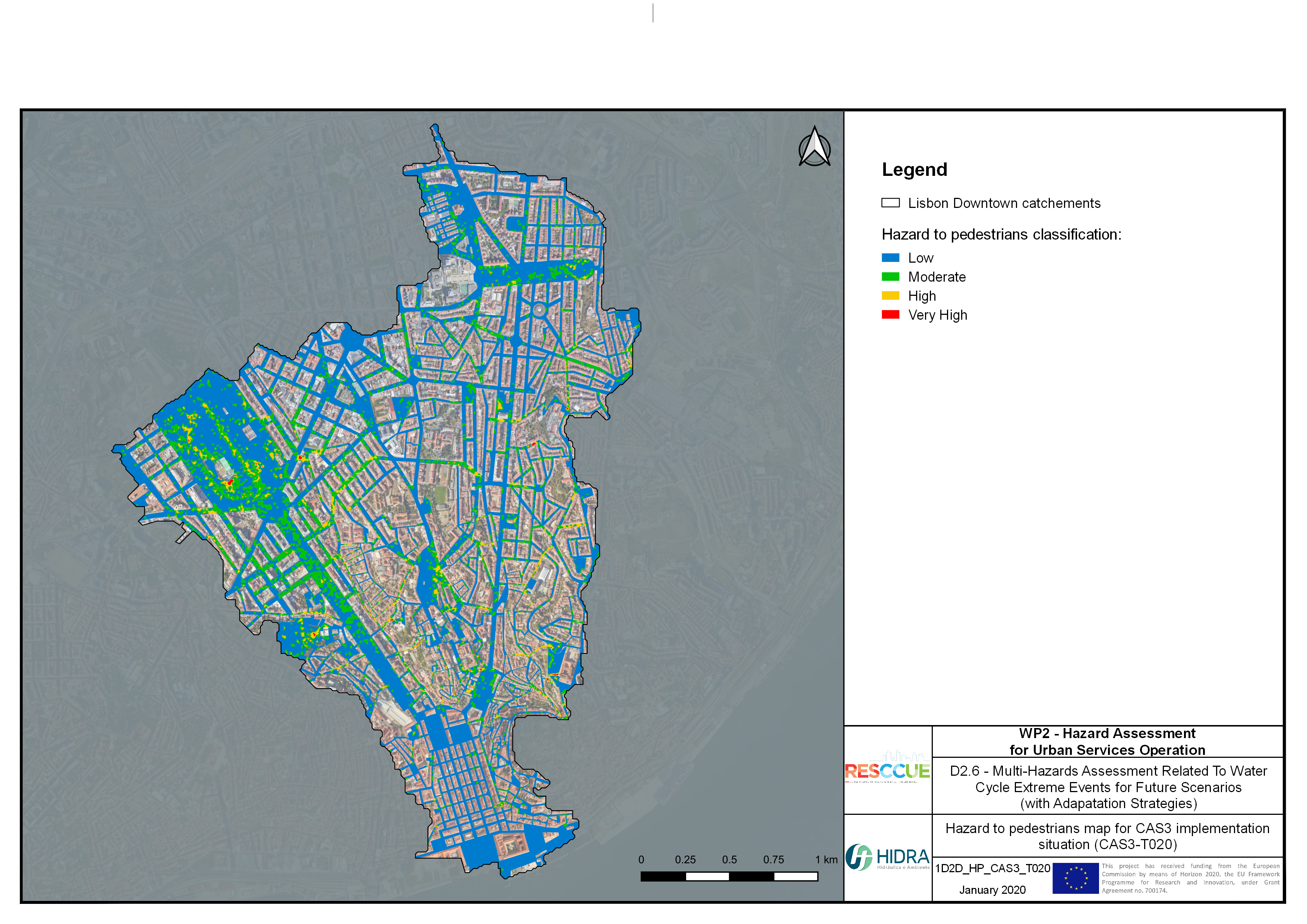
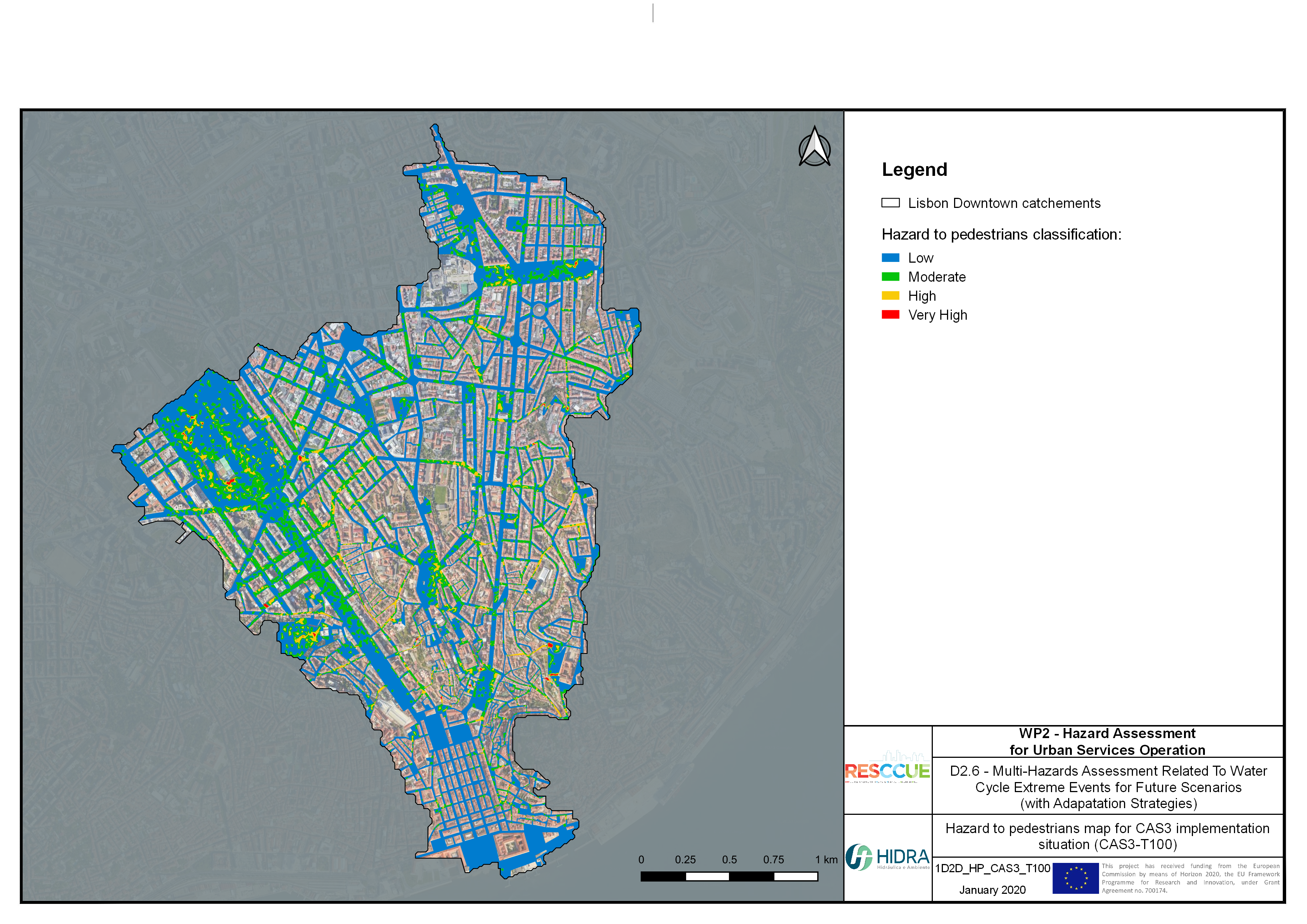
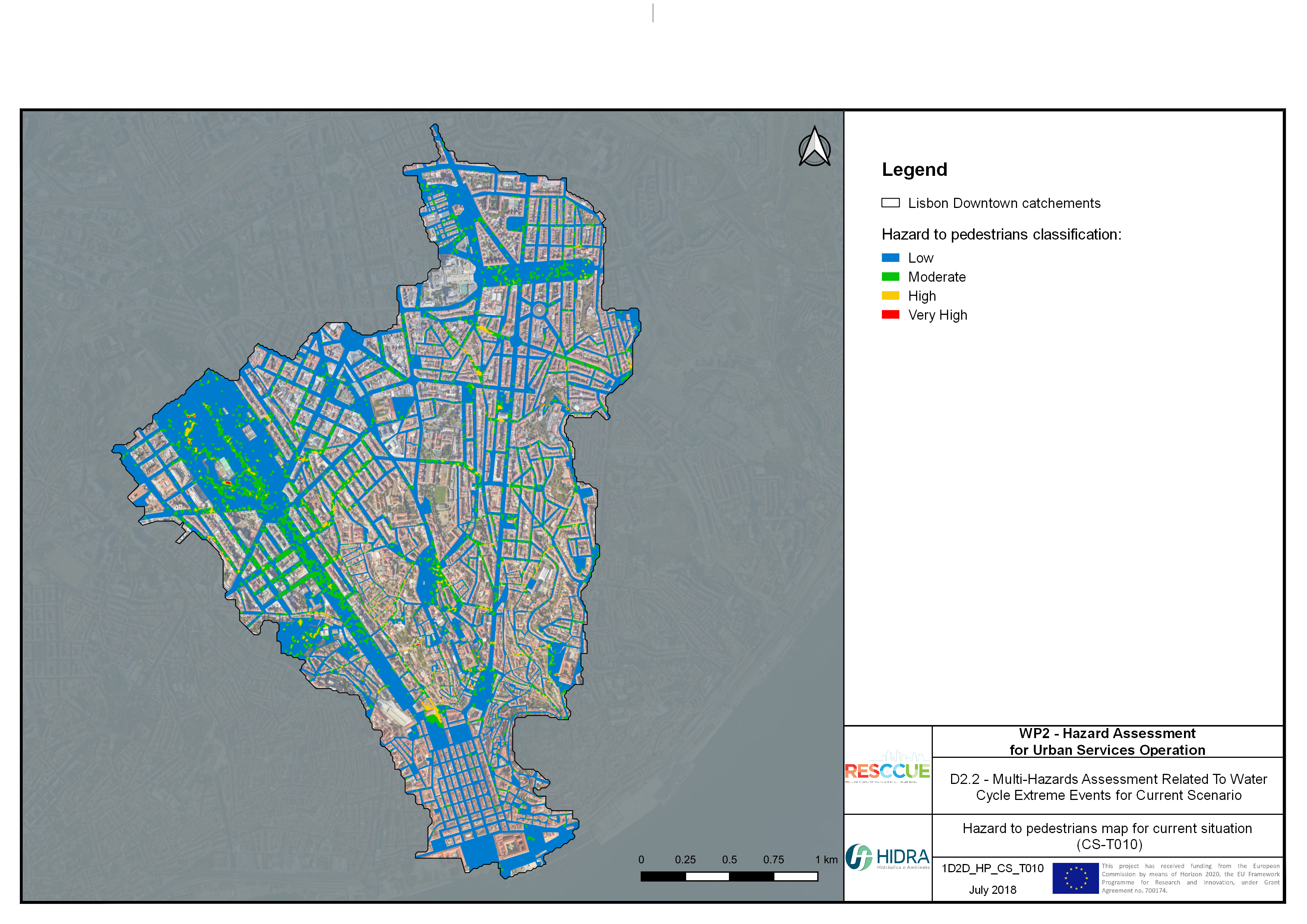
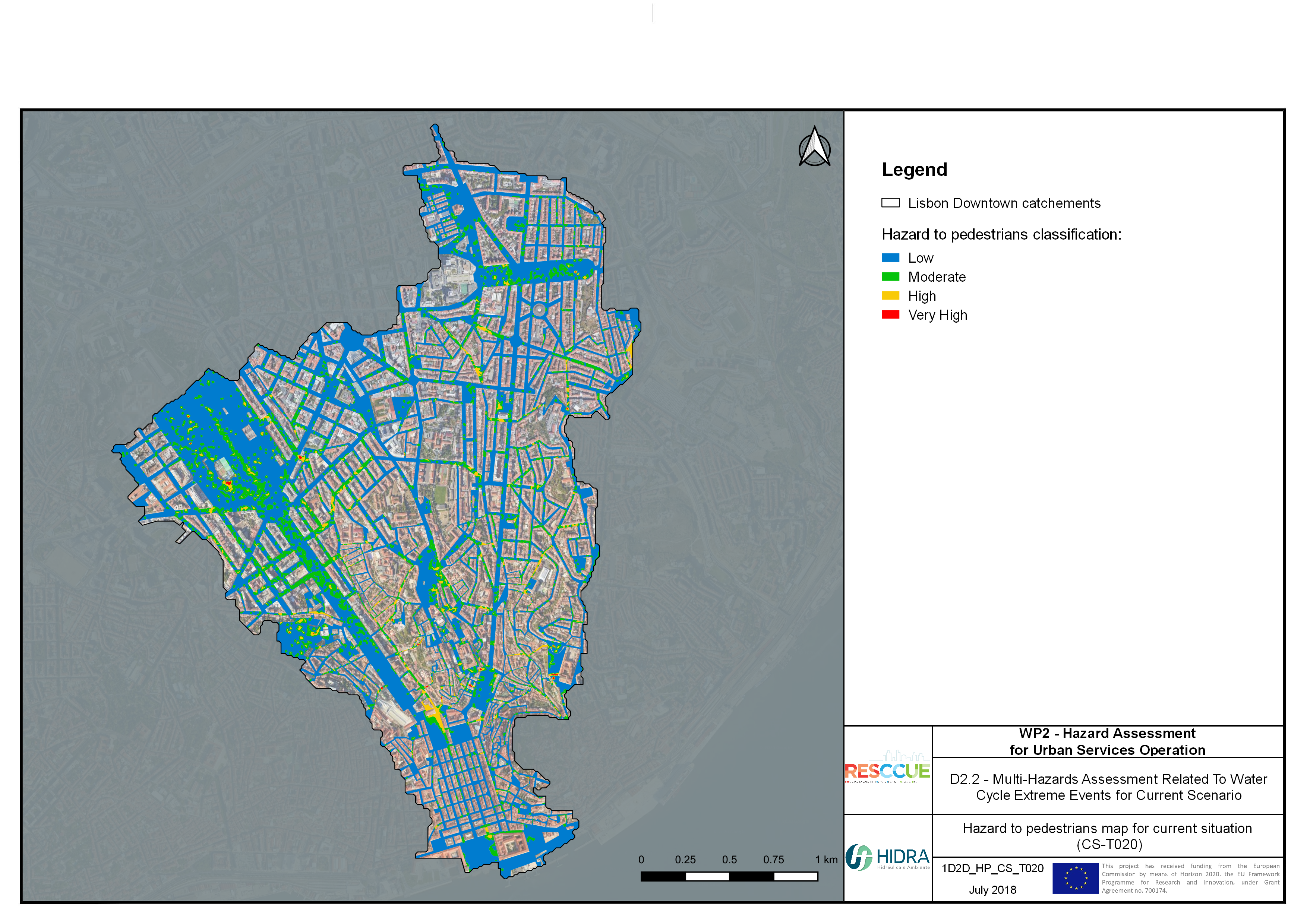
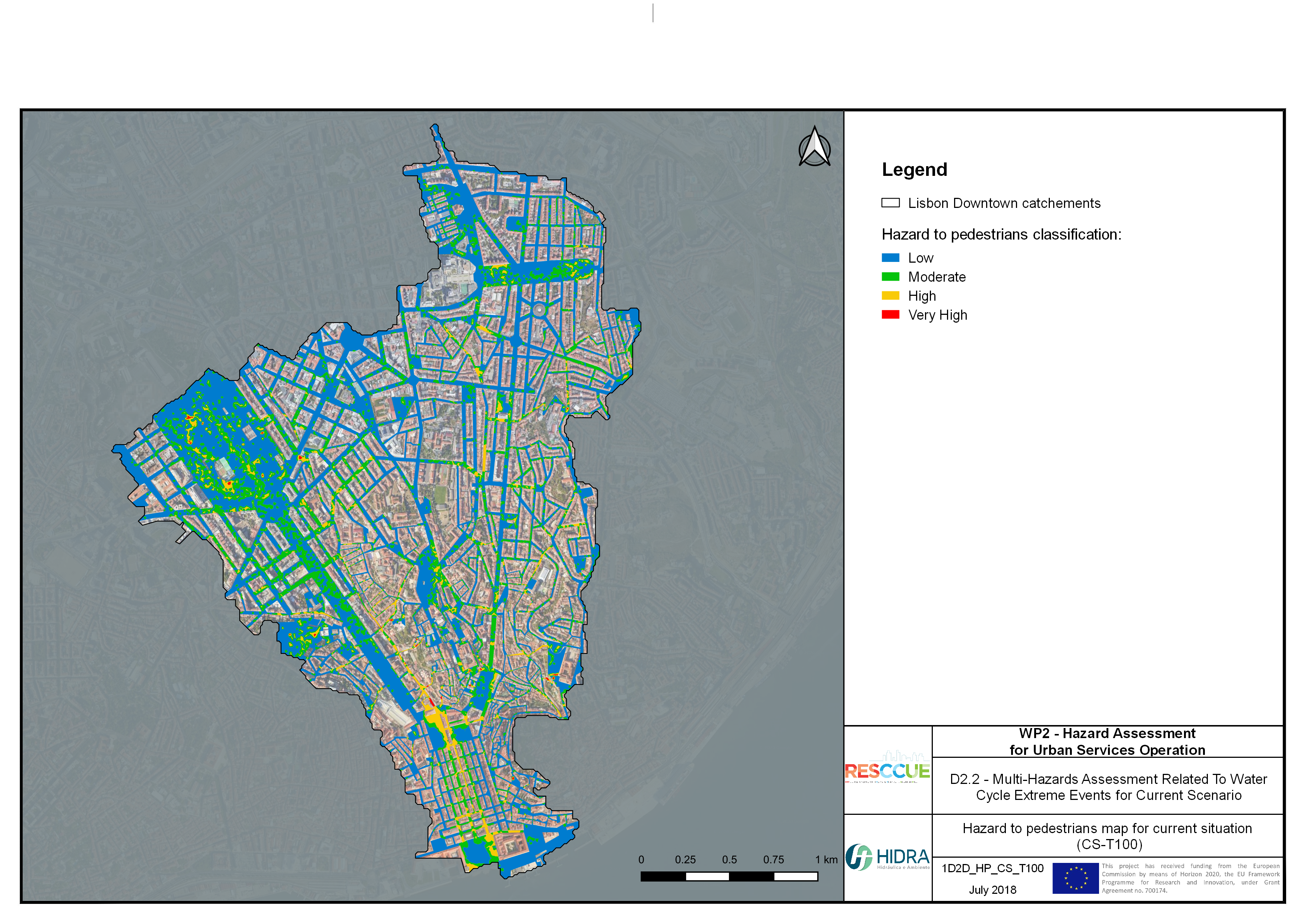
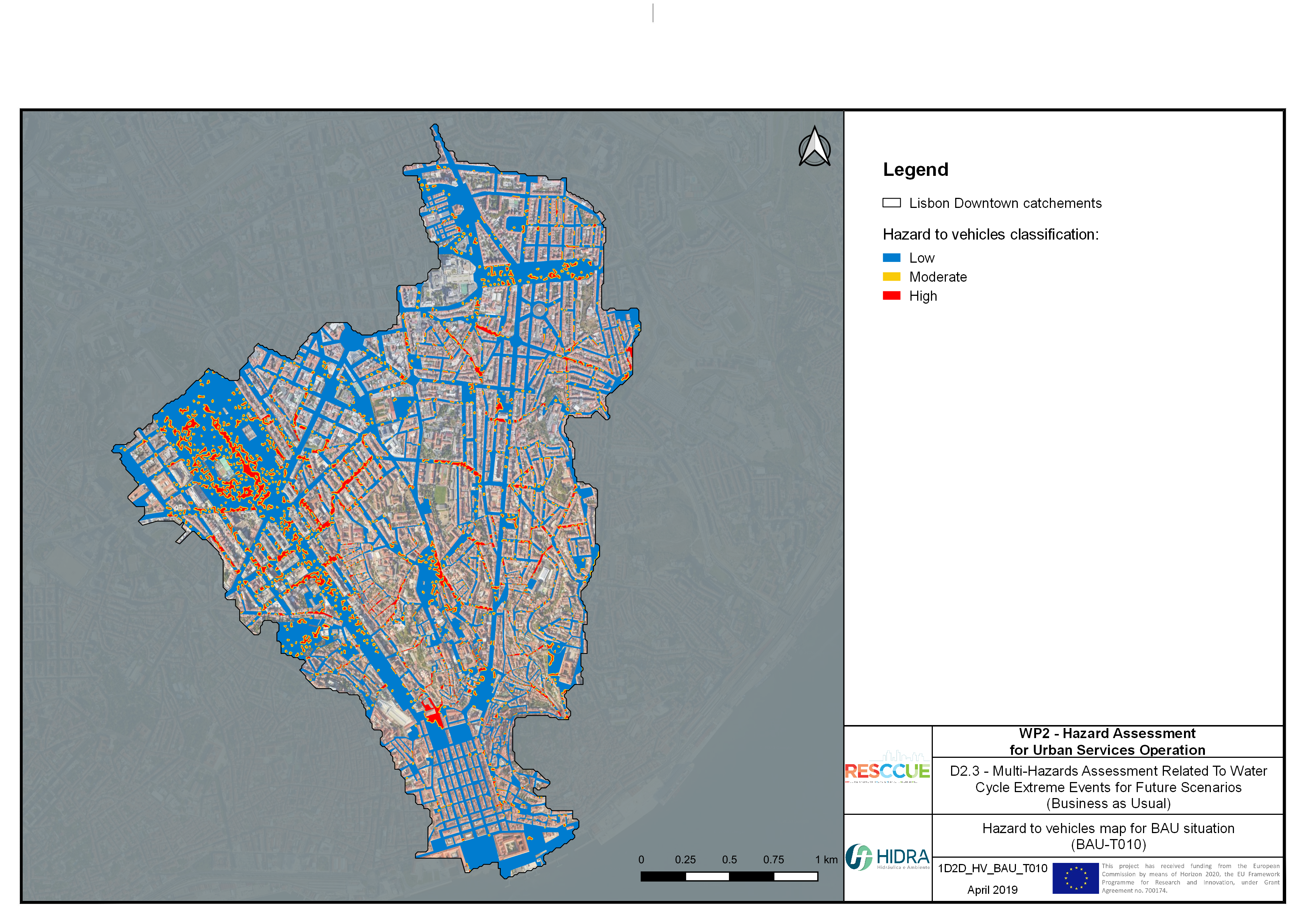
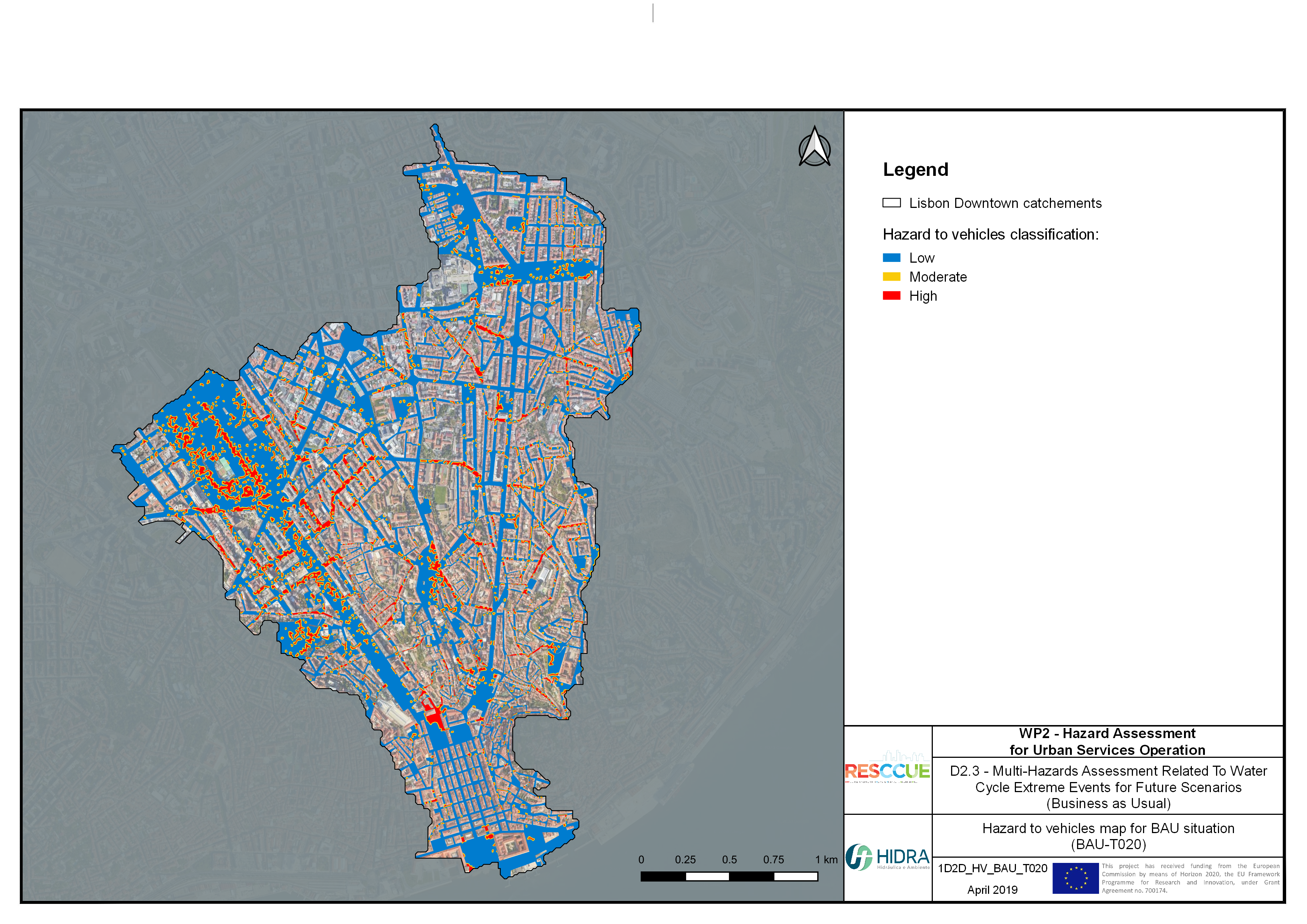
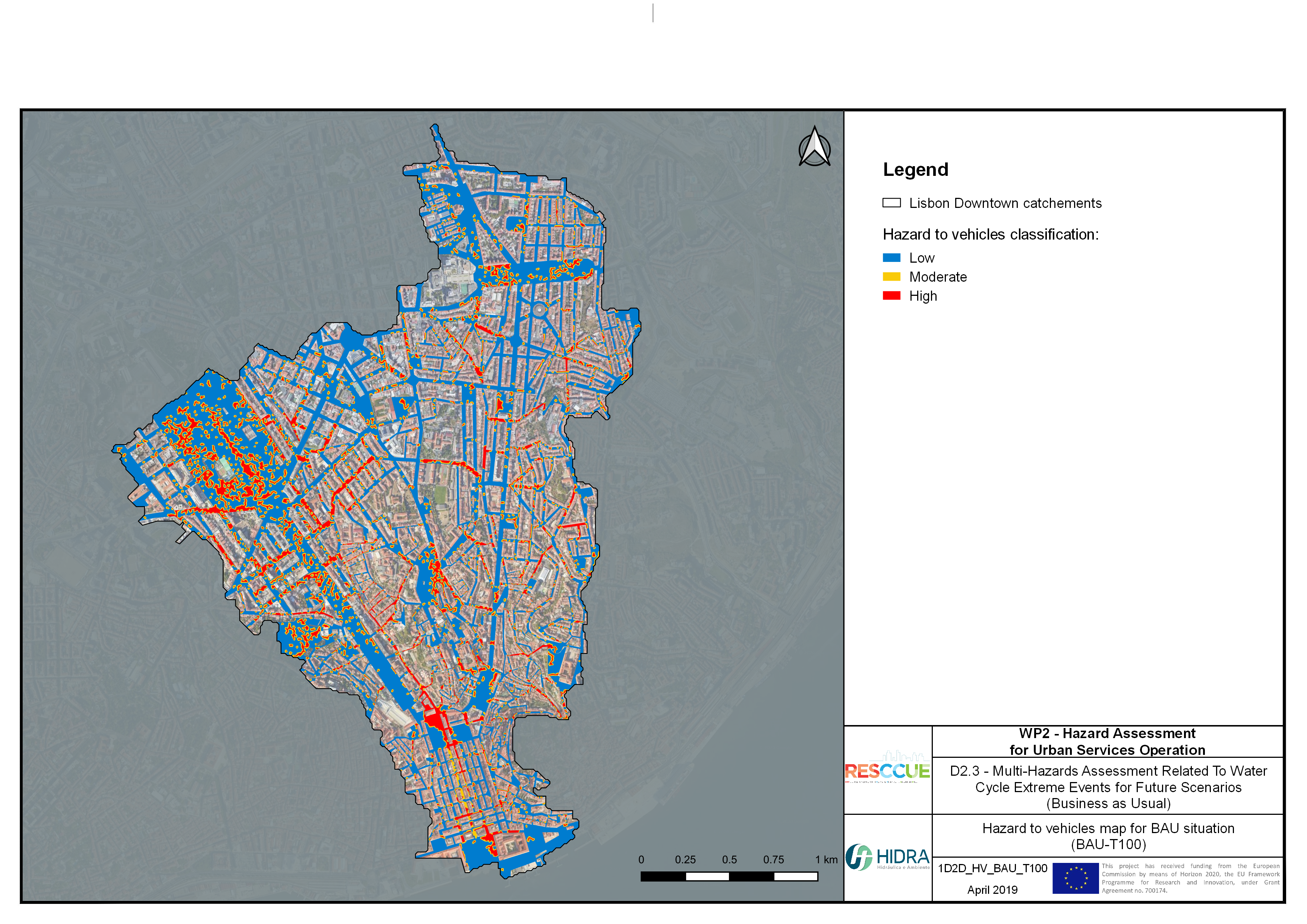
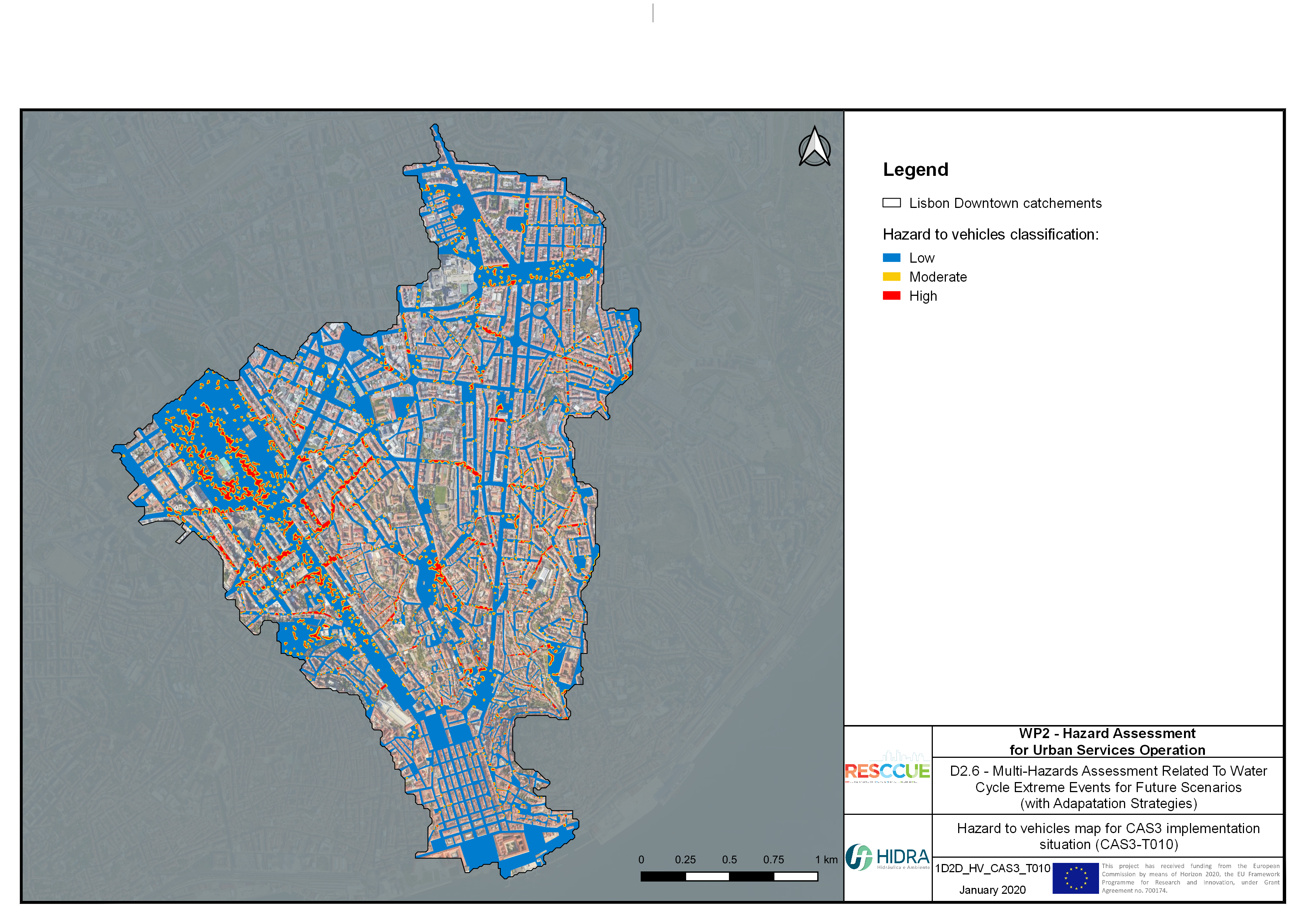
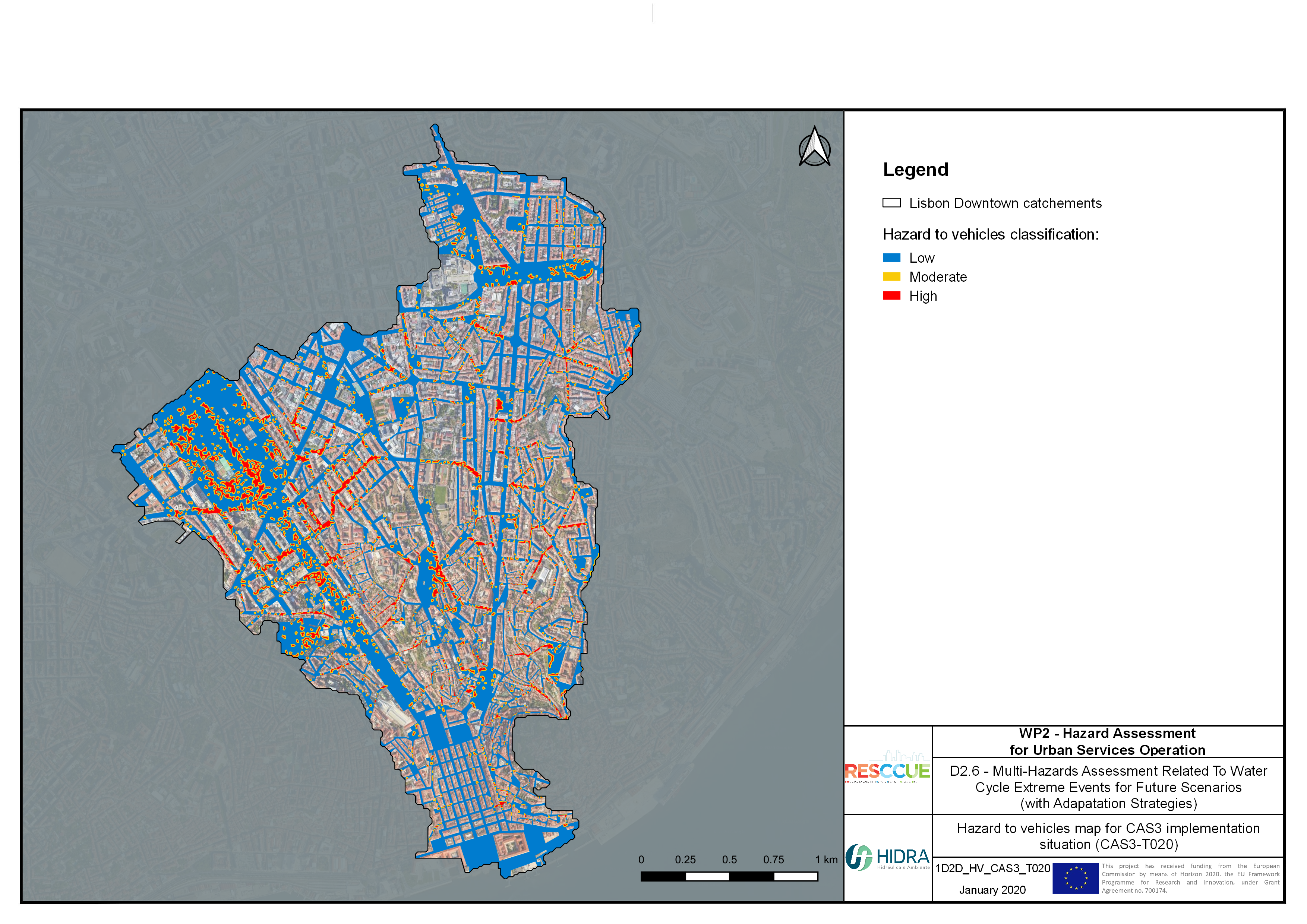
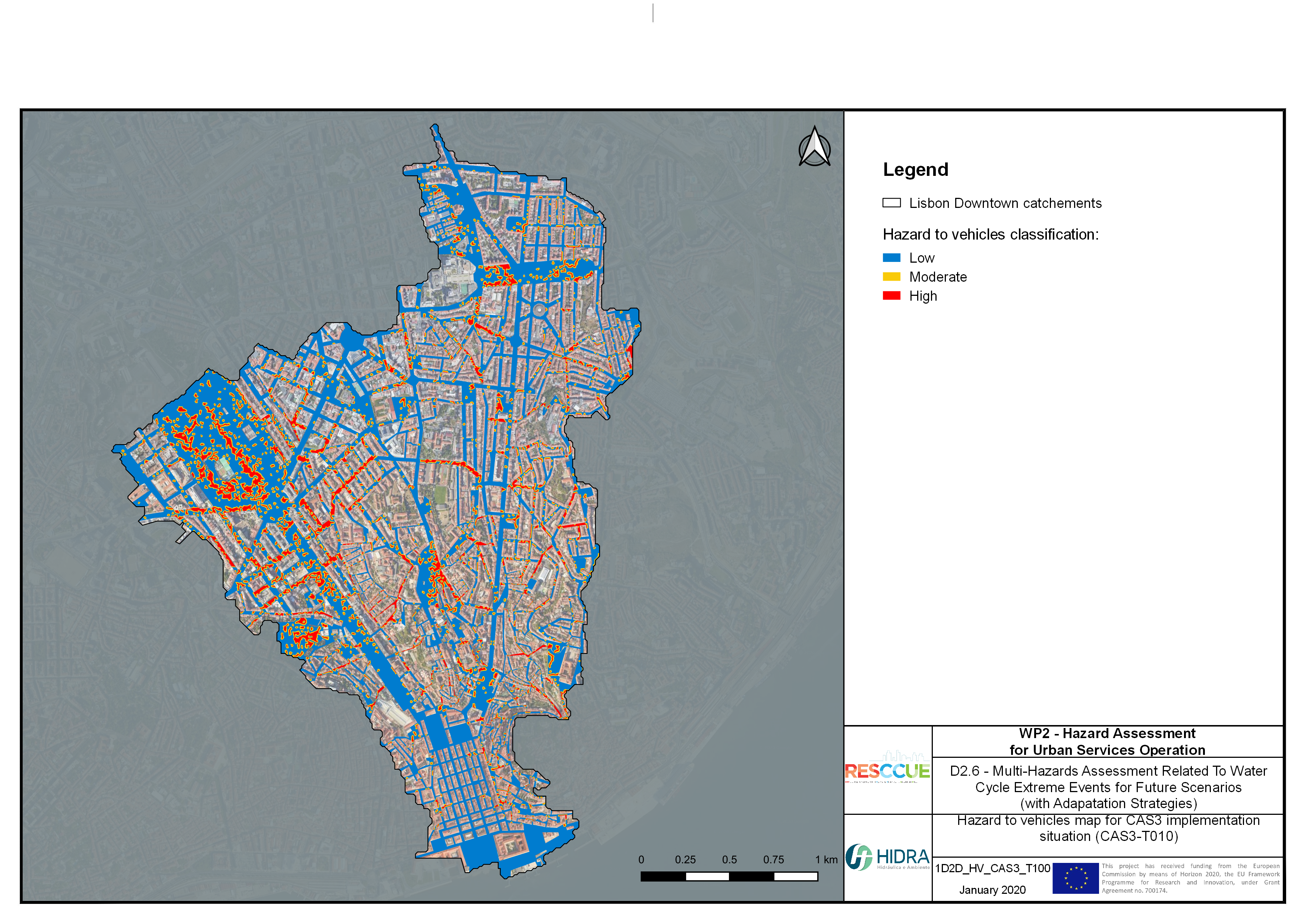
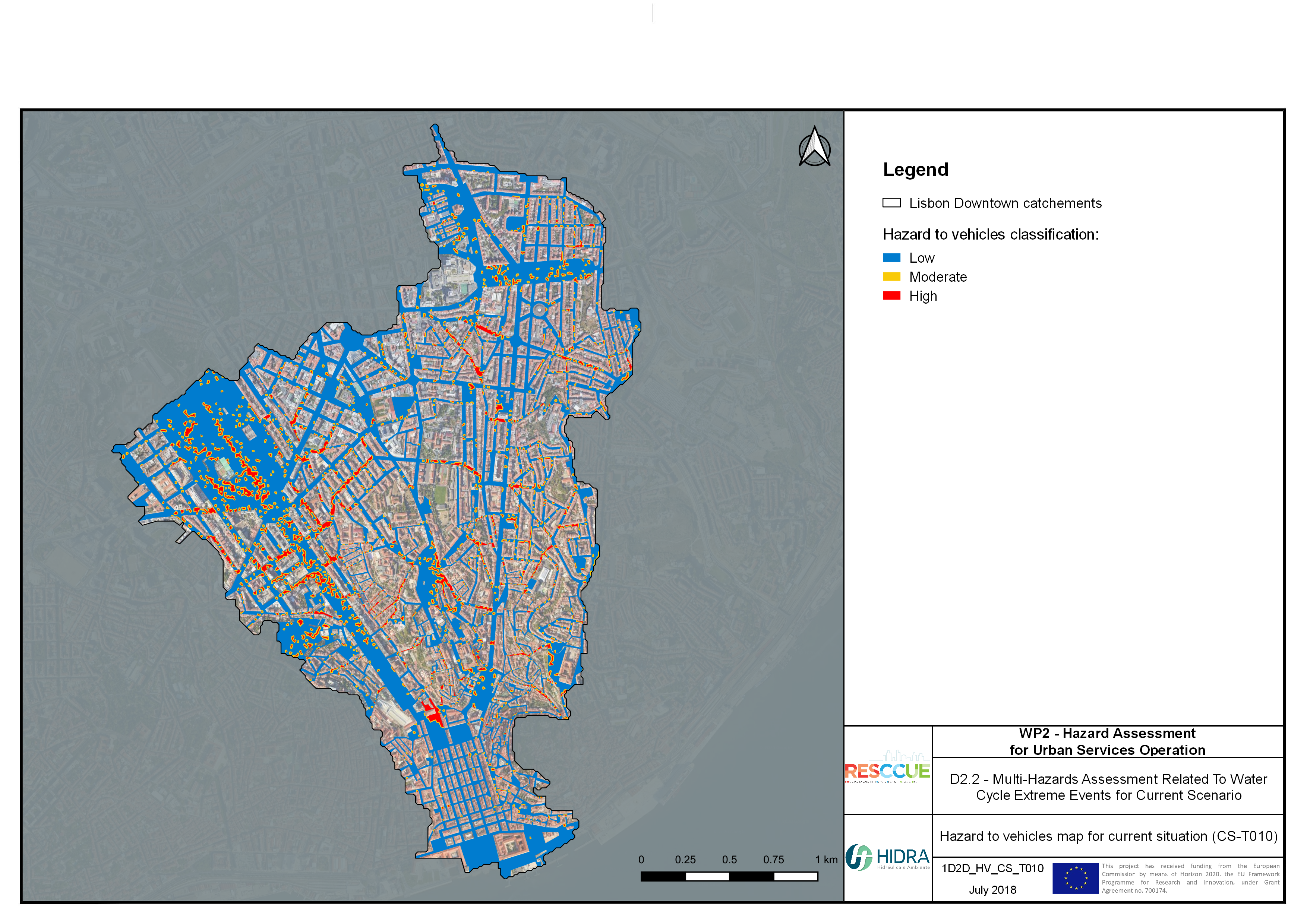
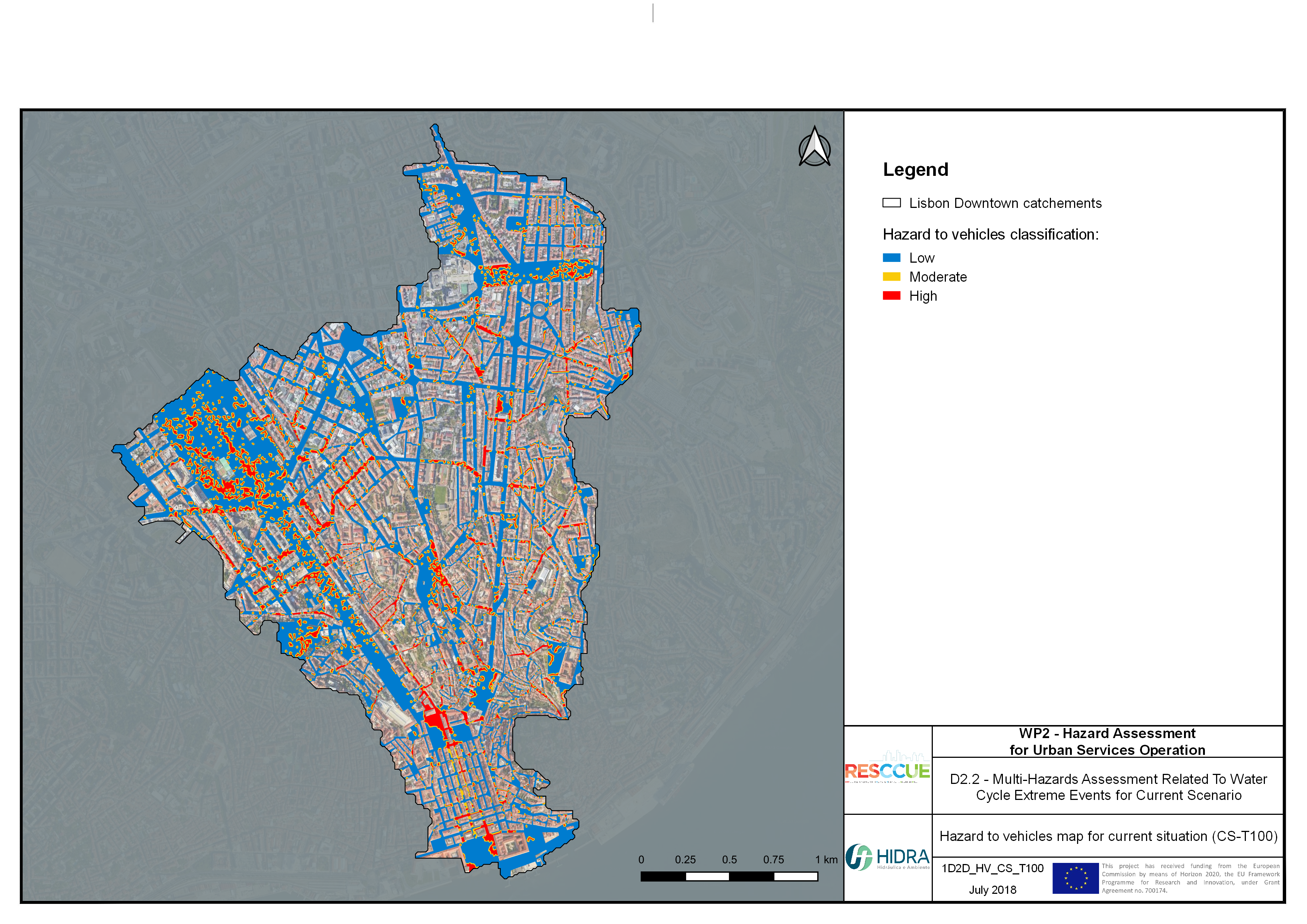
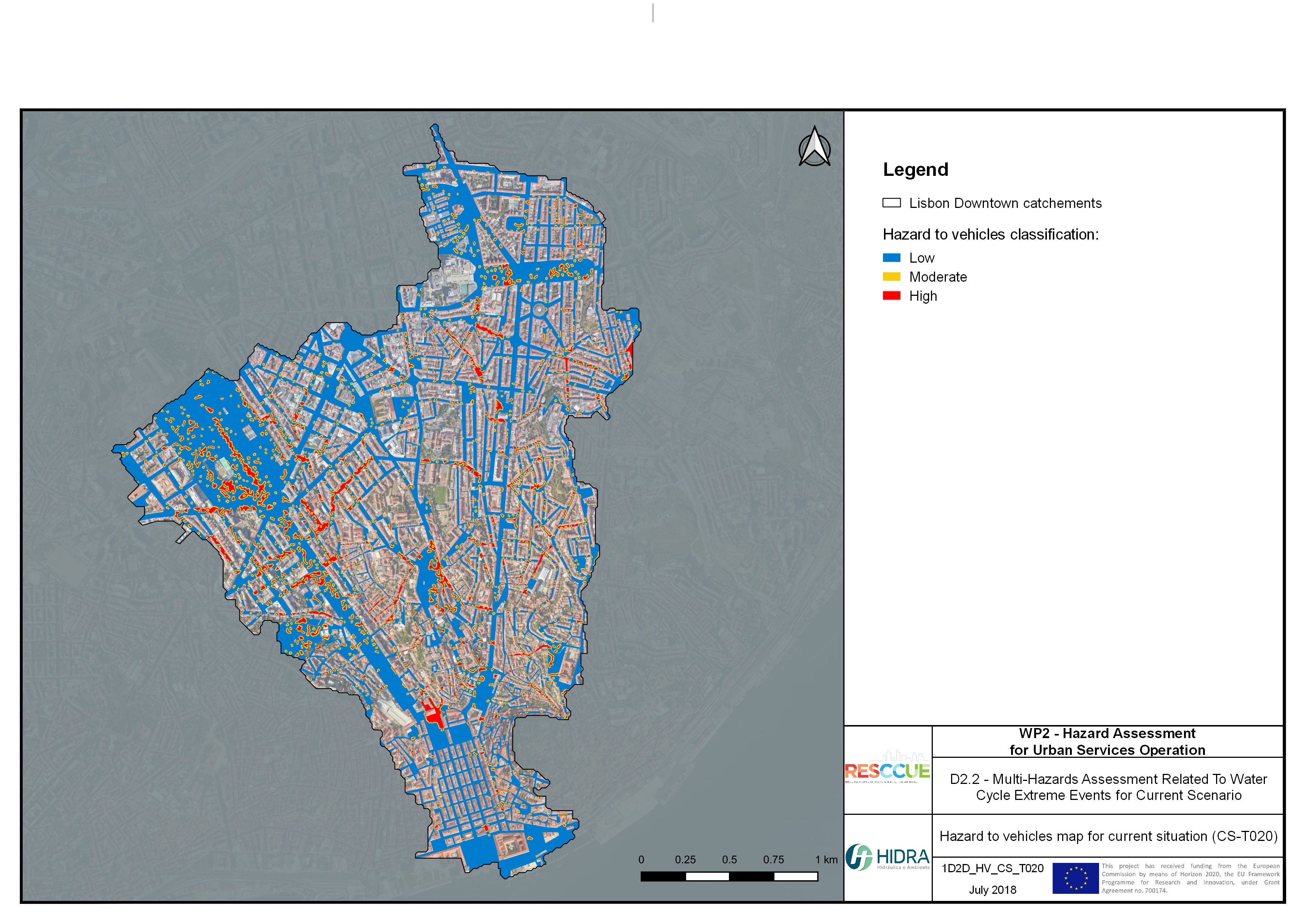
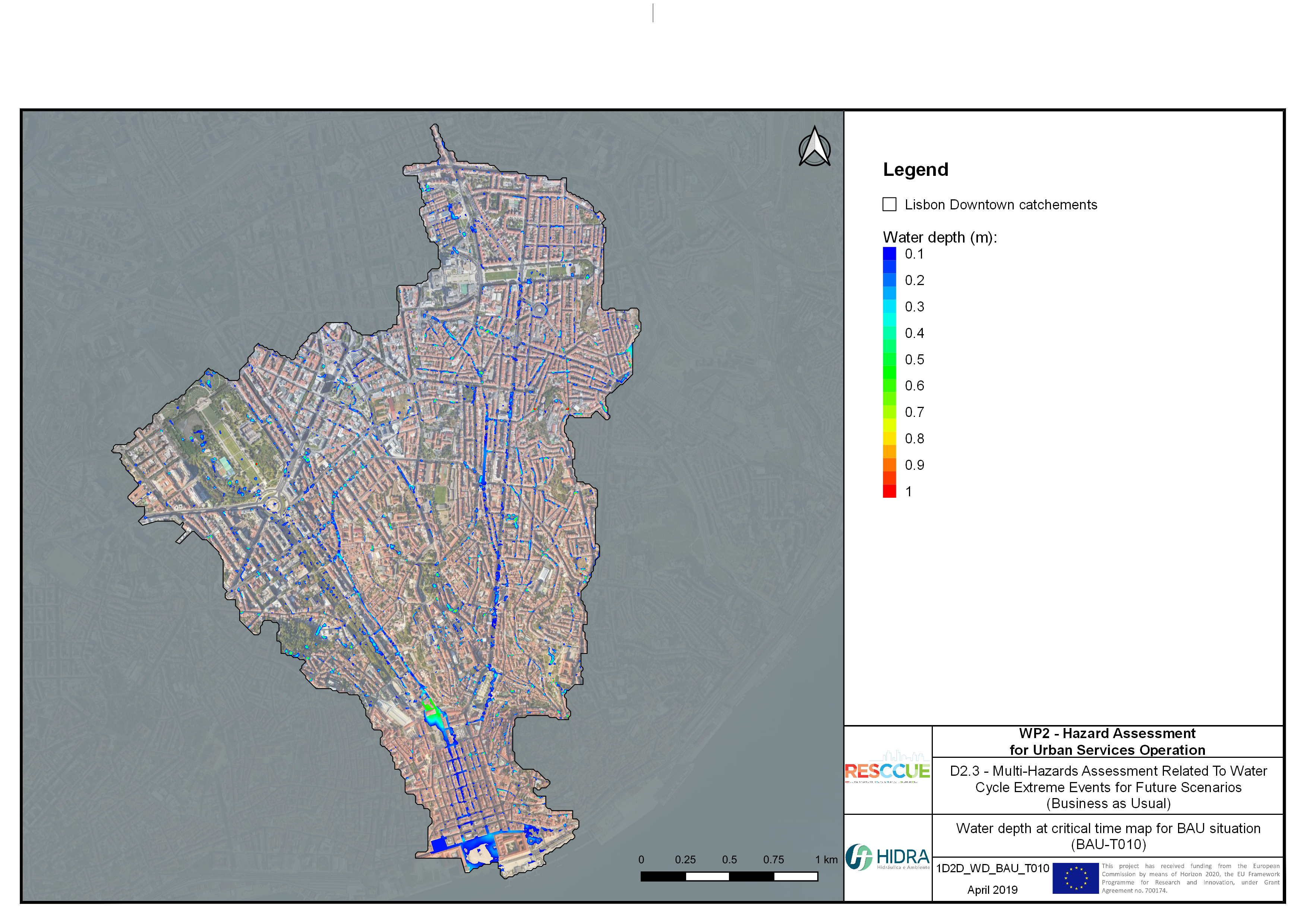
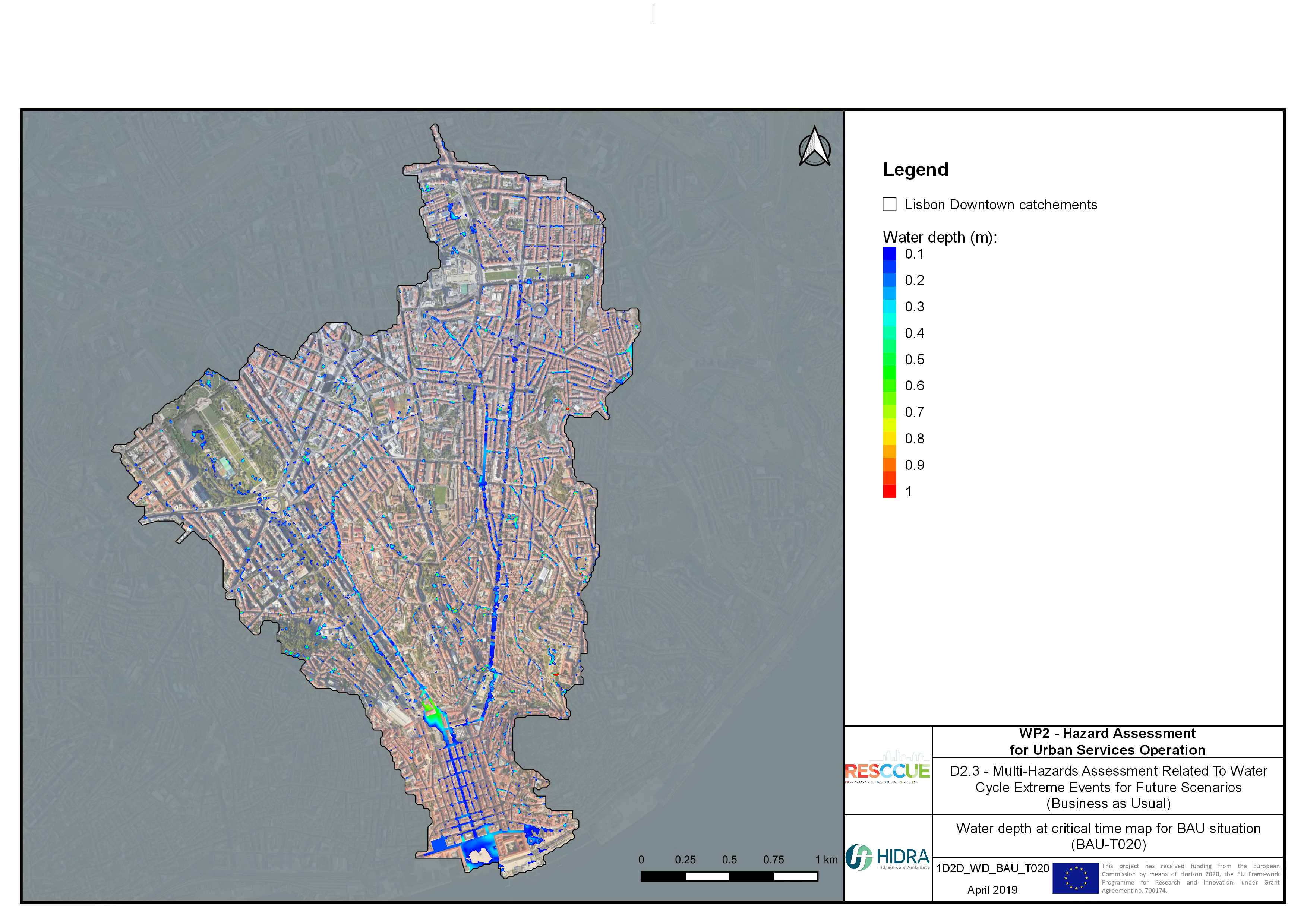
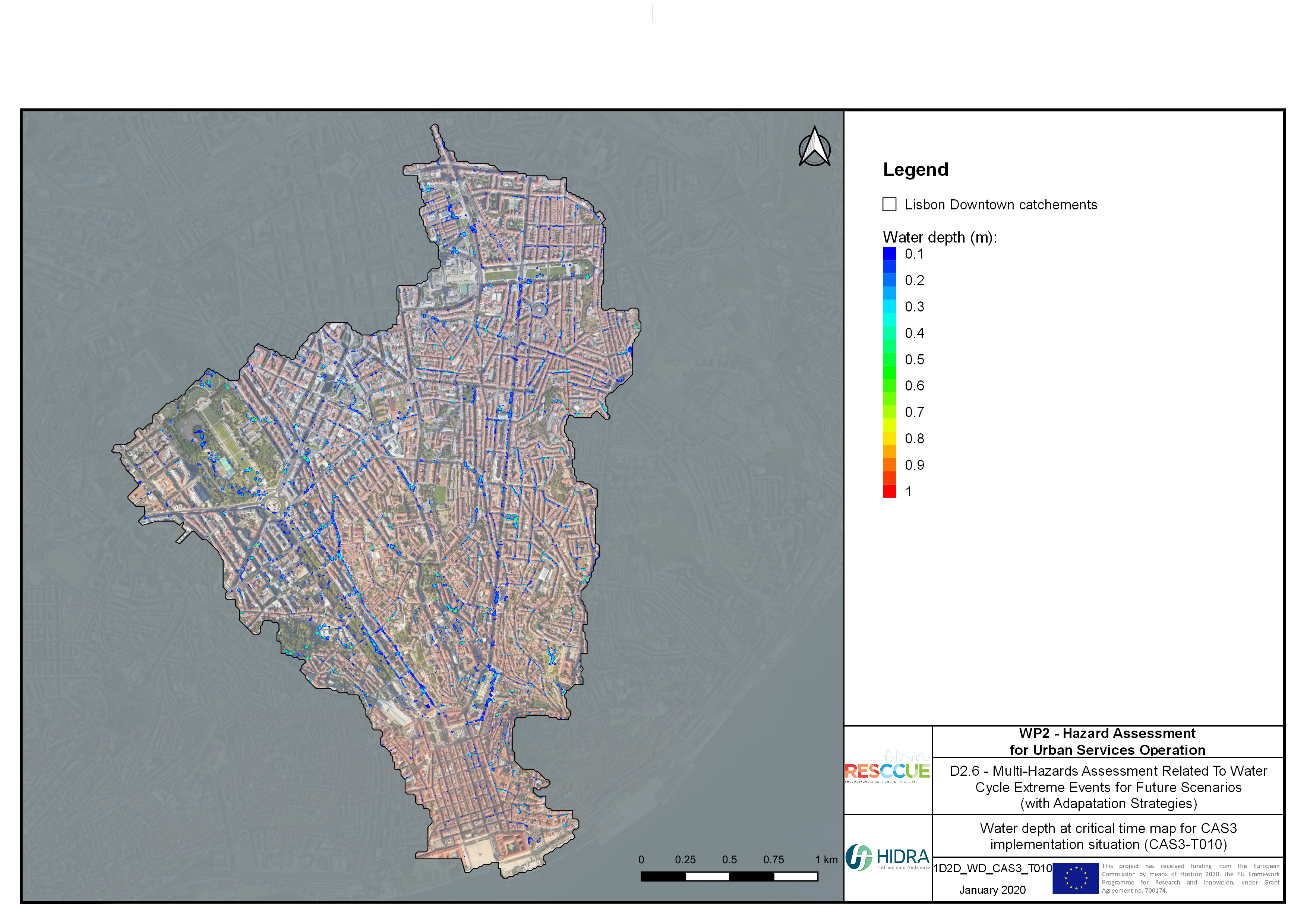
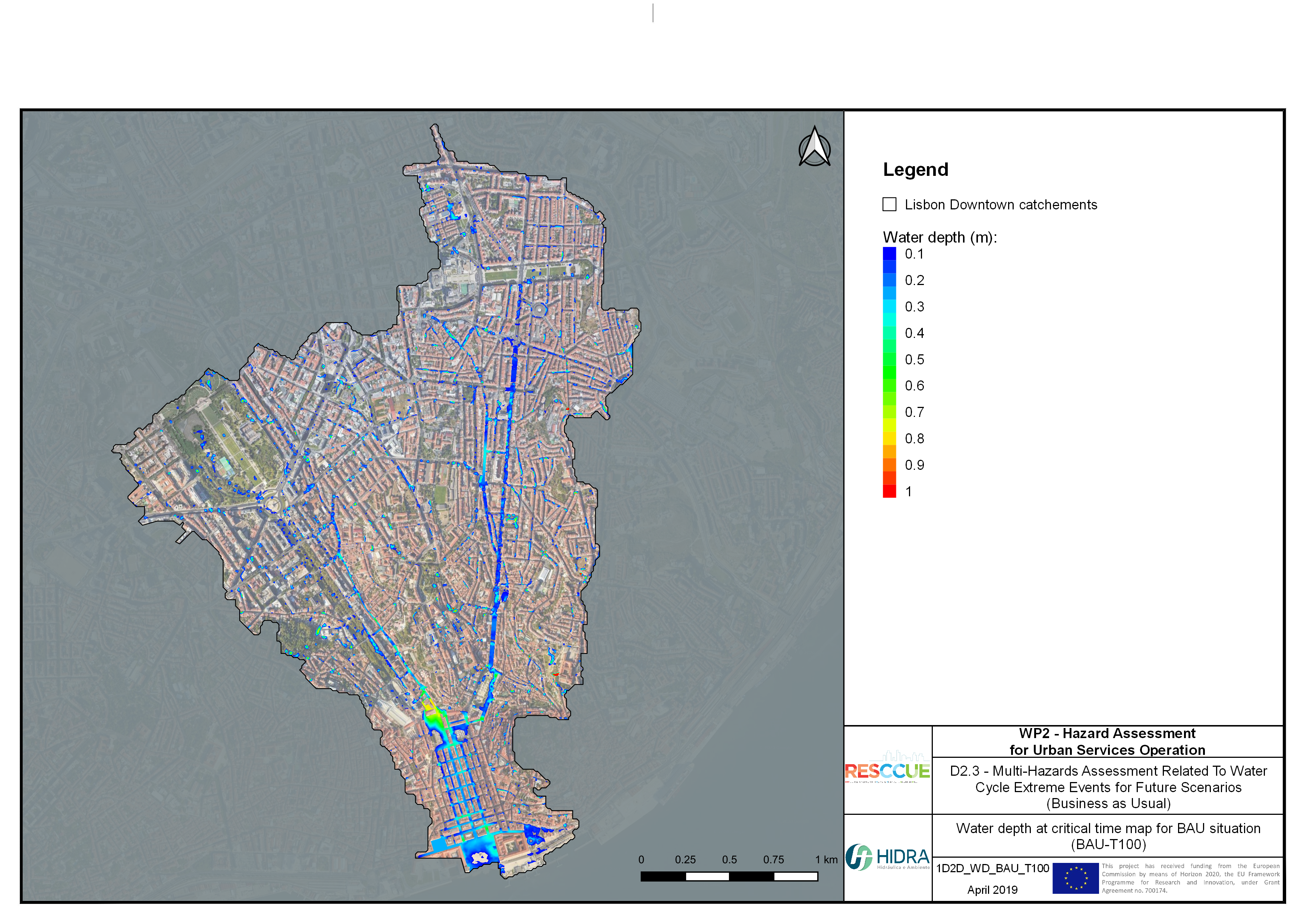
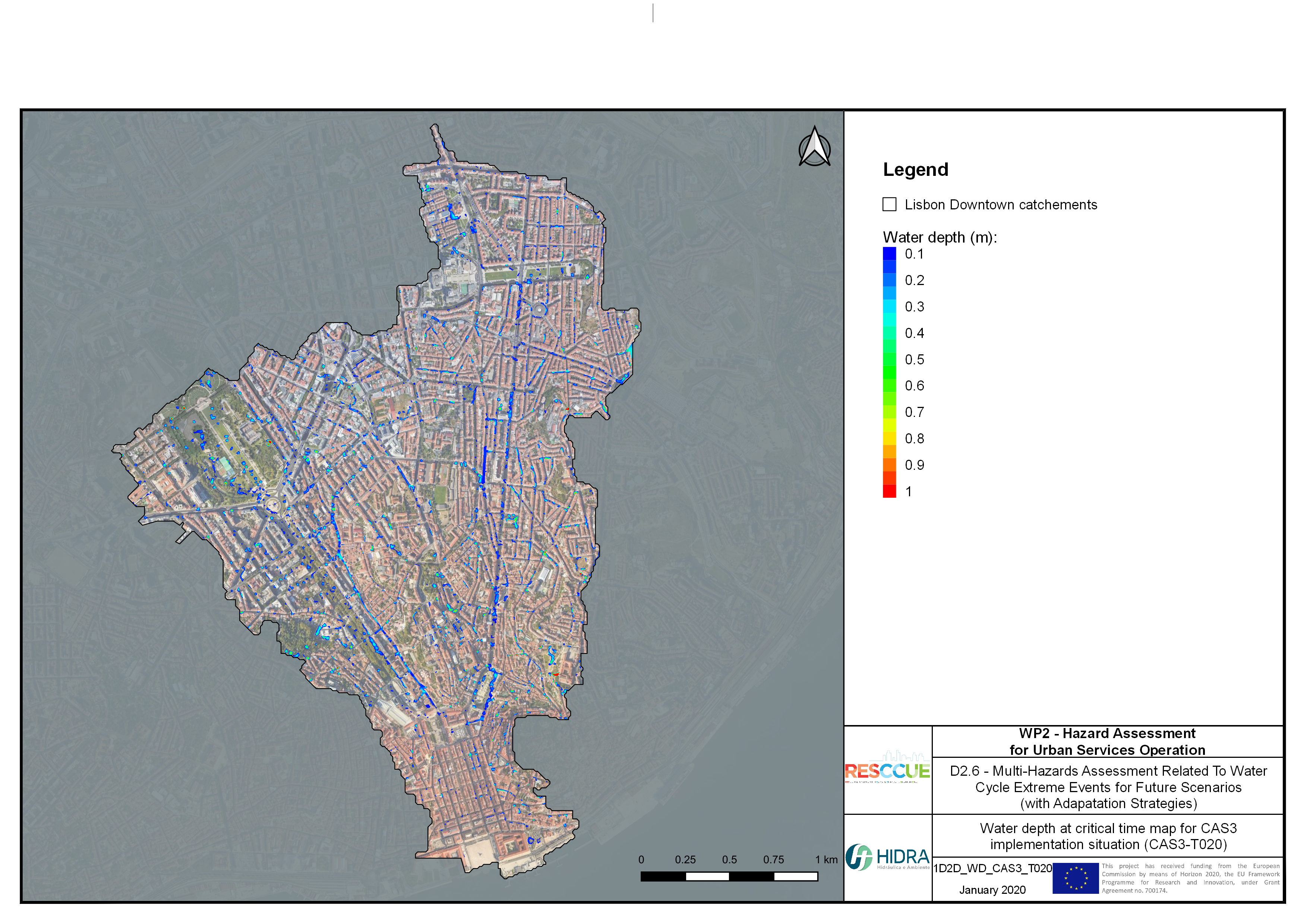
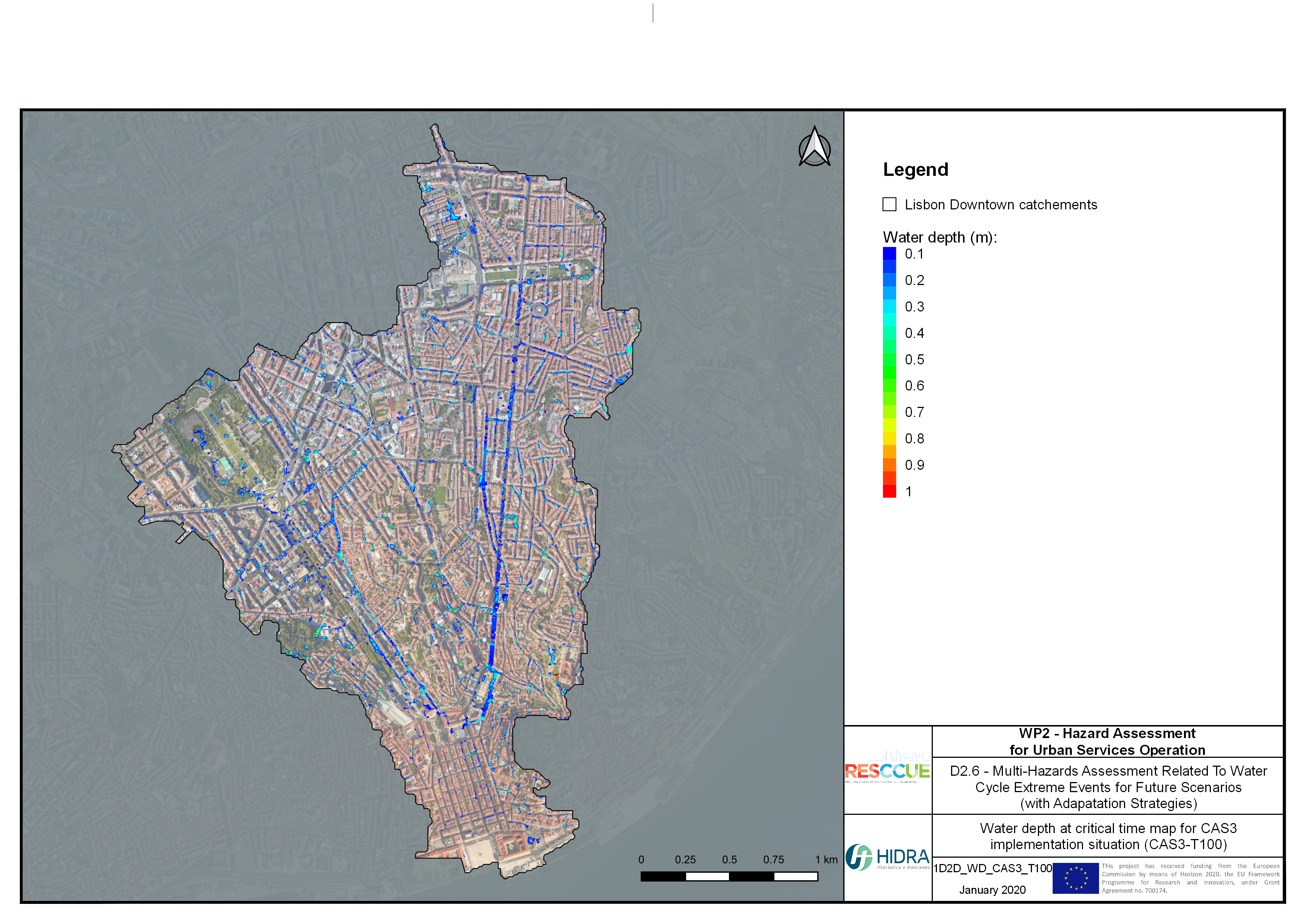
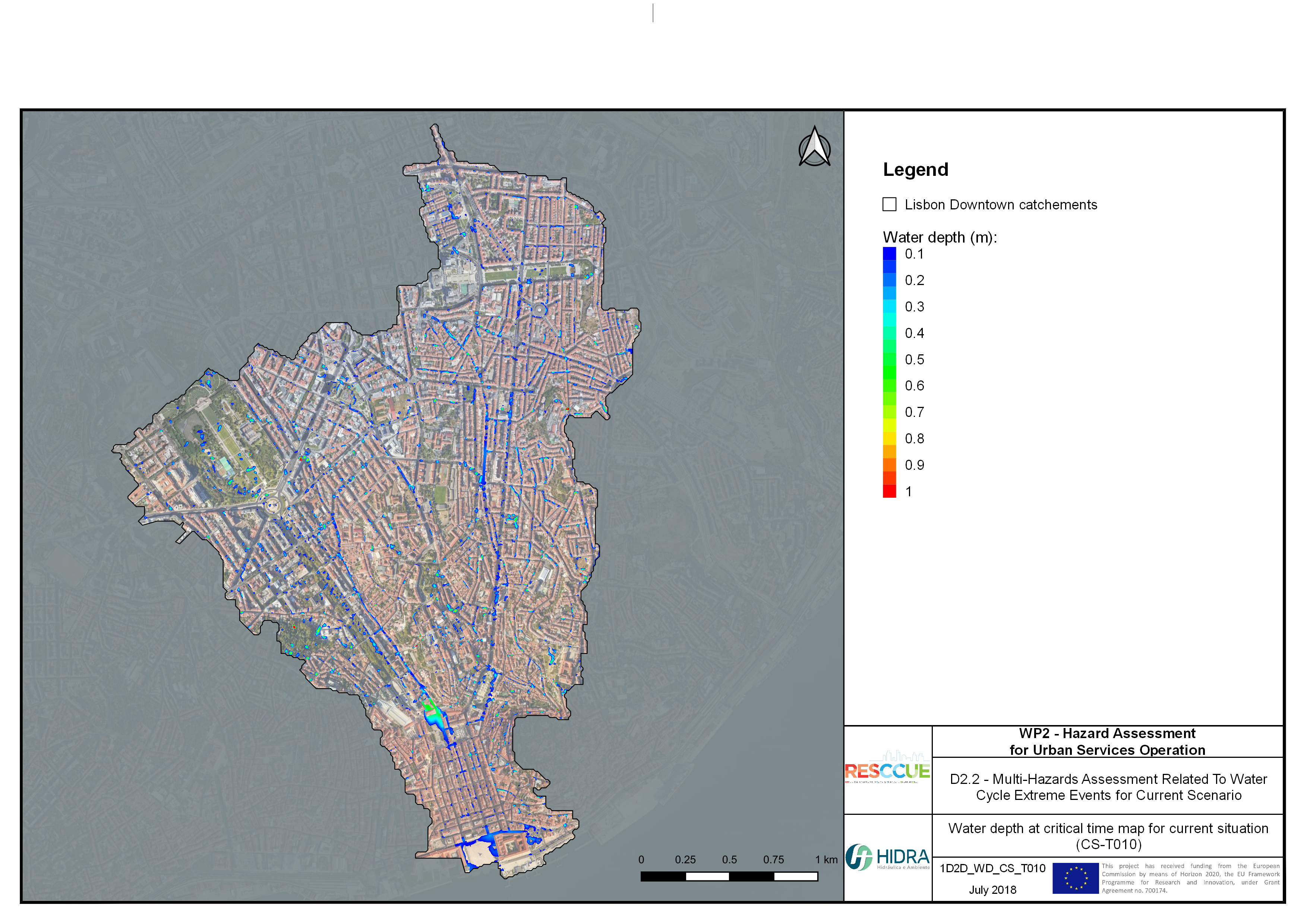
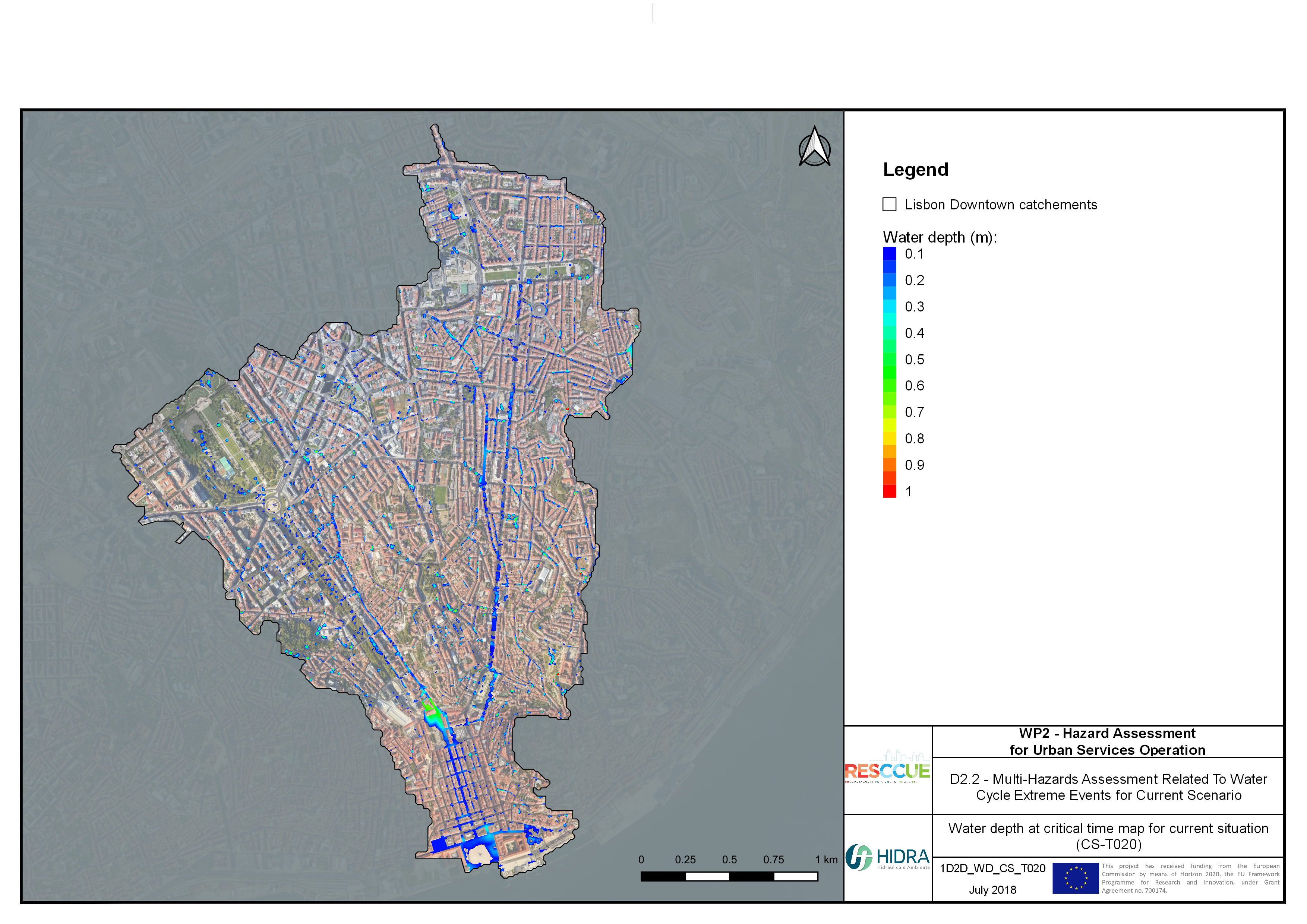
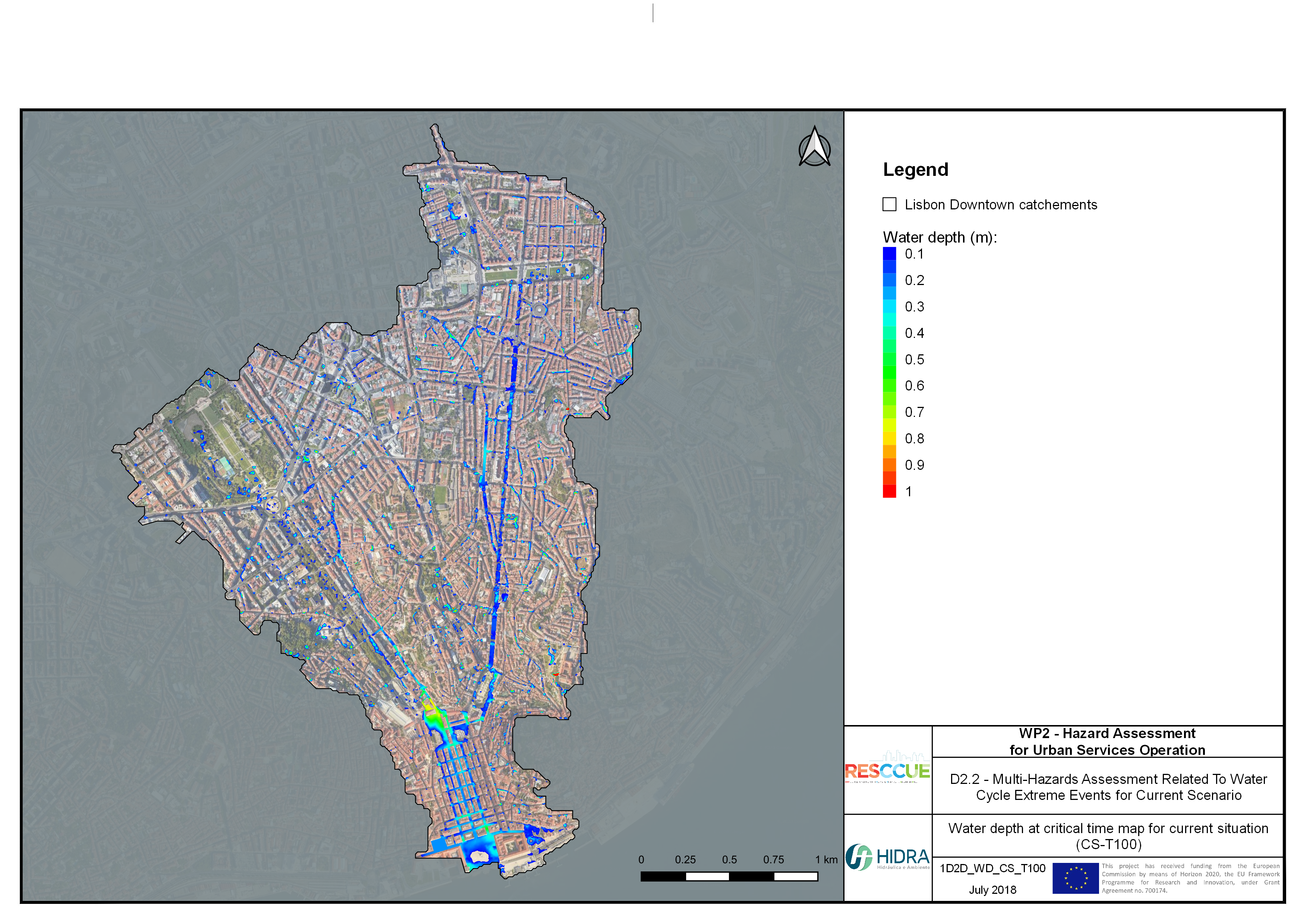
Flood hazard assessment in Barcelona, Lisbon, Bristol
Strategic urban services modelling
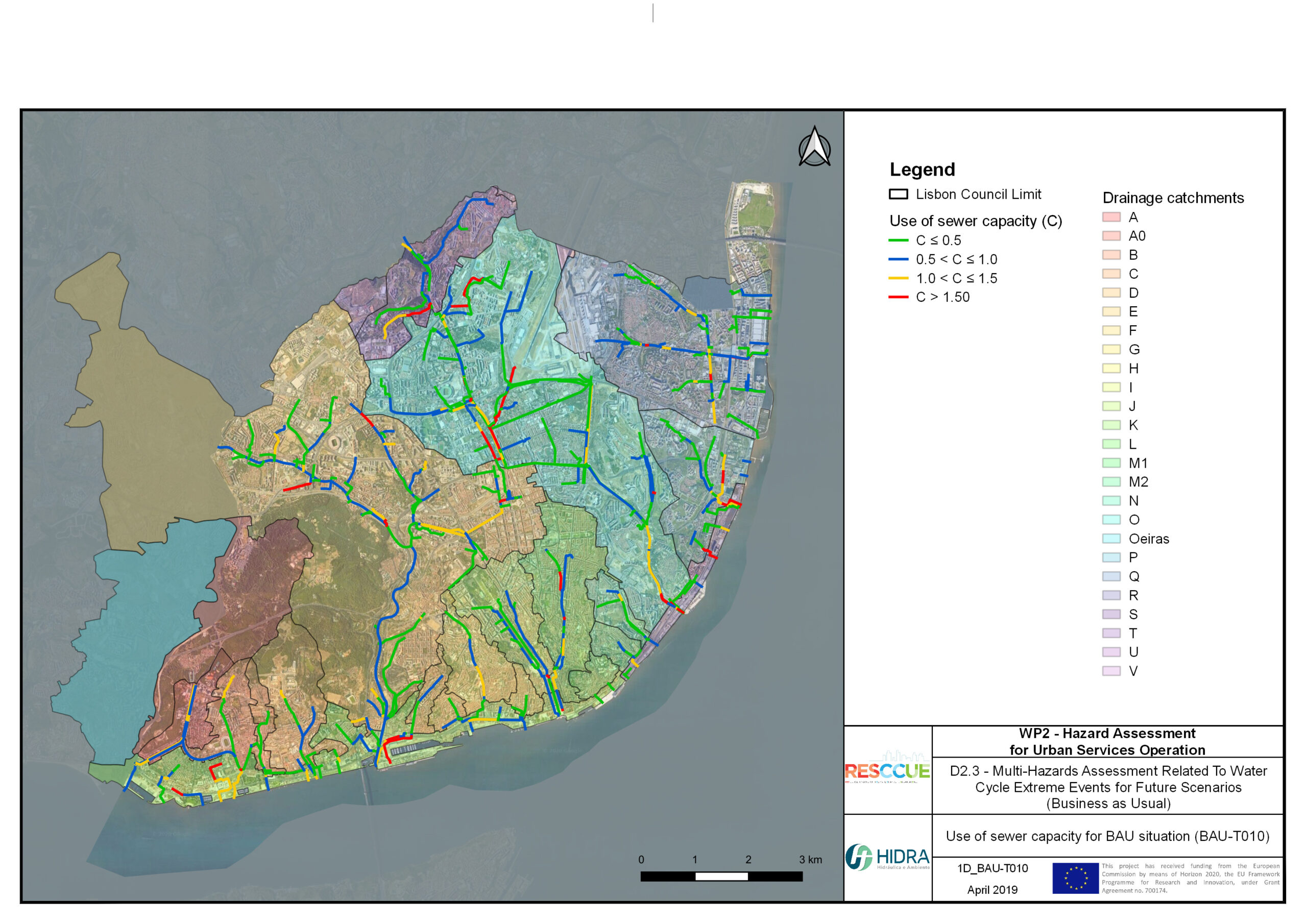
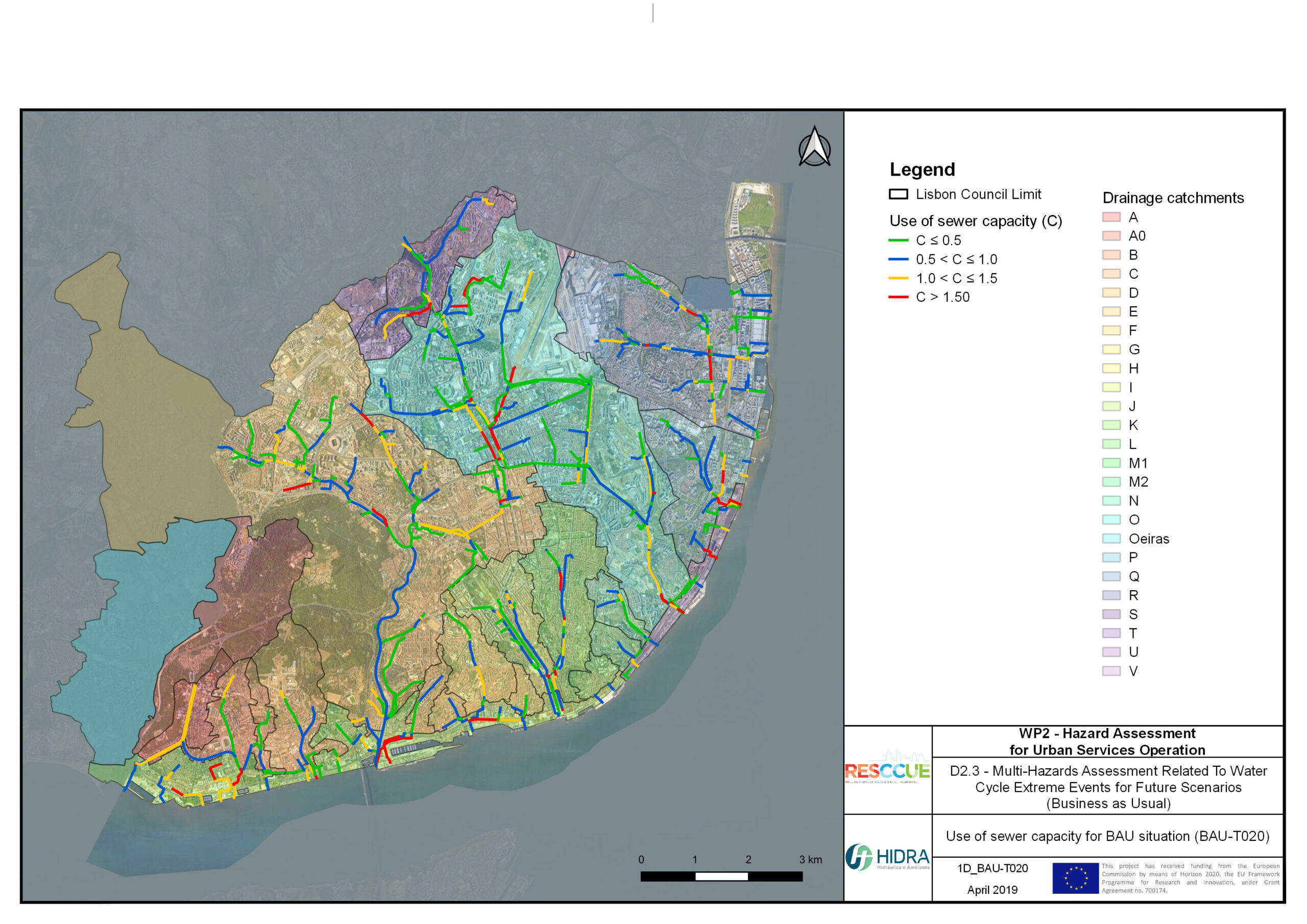
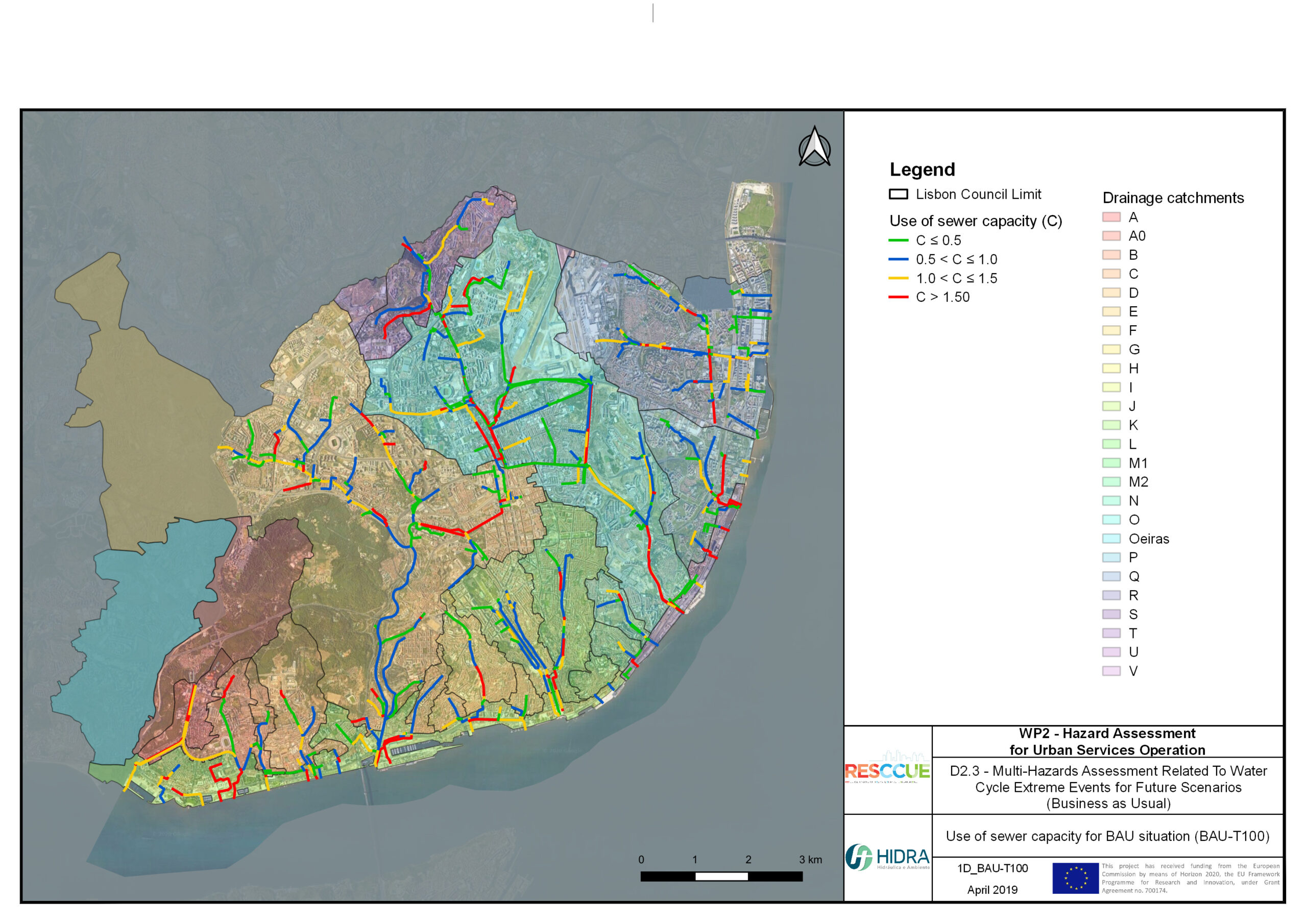
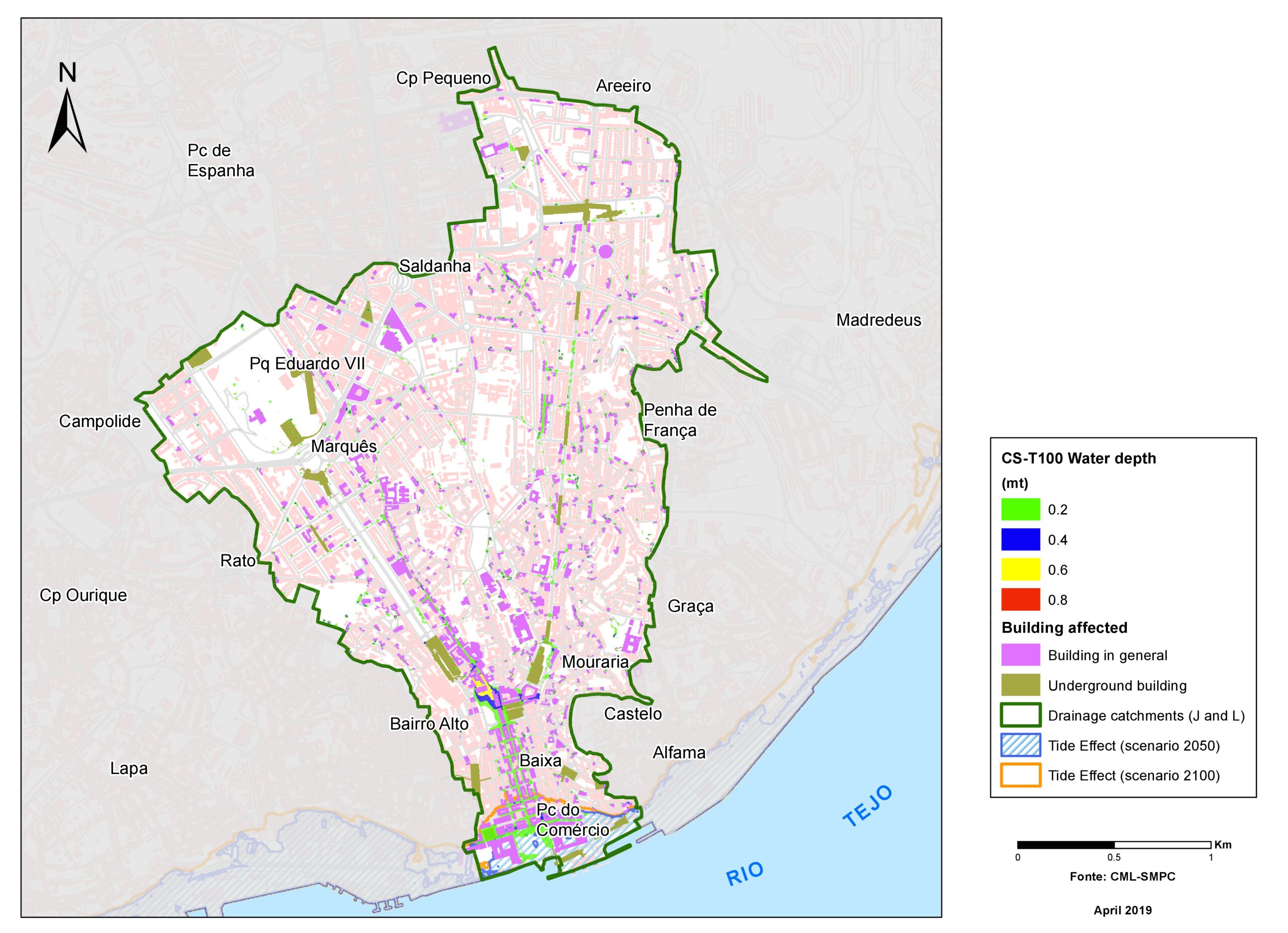
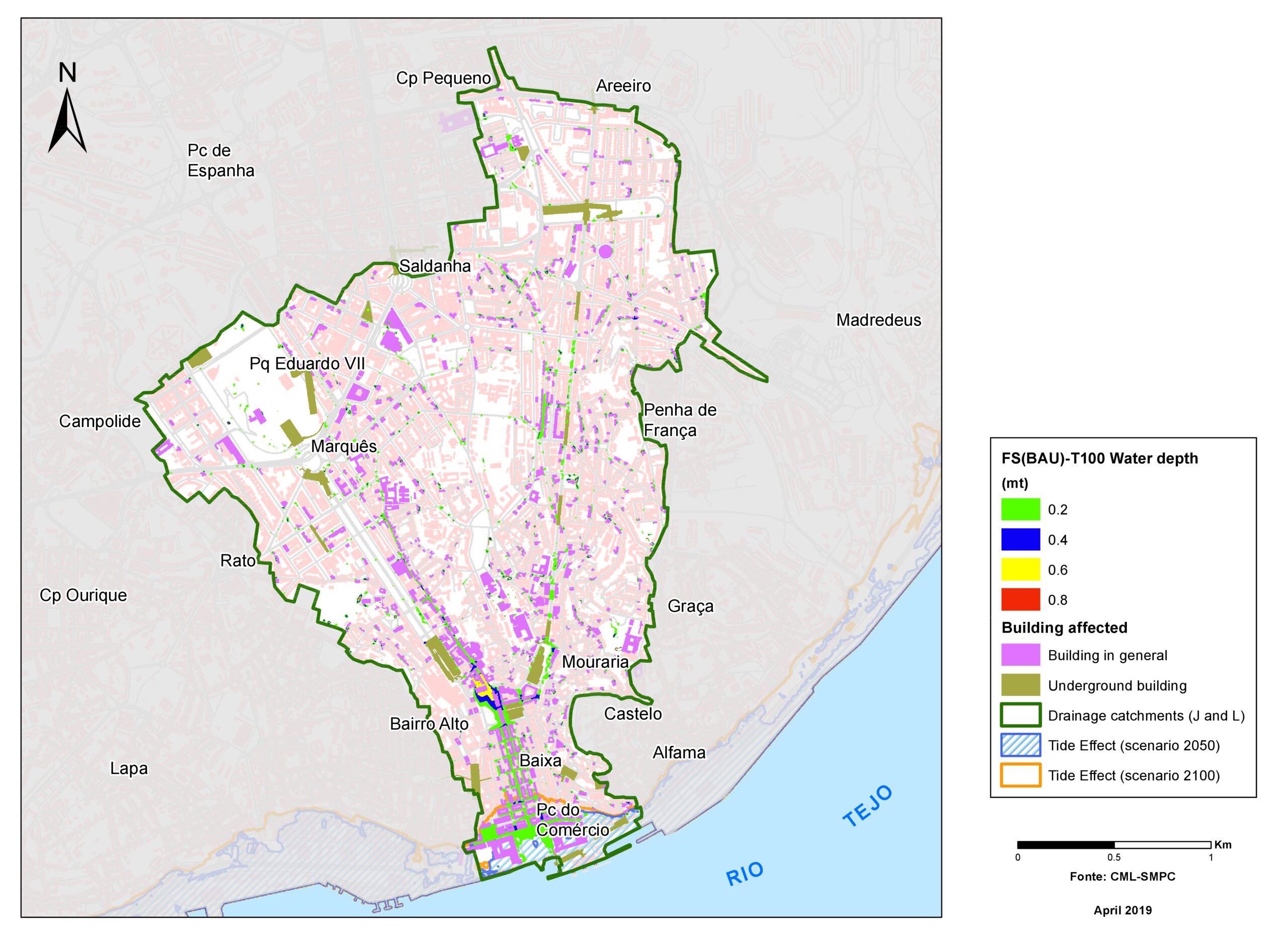
+The outputs of the hydrodynamic model (flood extension, flood depths and velocities) were used to generate flood hazard maps for pedestrian and vehicles according to experimental hazard criteria. Simulations were performed for different return periods related to current and future scenarios (including Business as usual and Adaptation scenarios) obtaining a specific hazard map for each case.